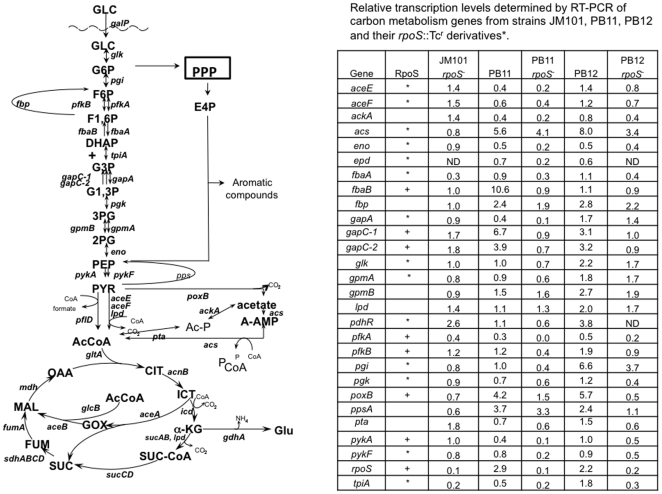
Figure 1. Central metabolic routes in the PTS− strains showing key metabolites and the genes involved in their transformation.
PTS, (not shown in the figure) is involved in the wild type strain in glucose transport and phosphorylation, using PEP and producing pyruvate. RTPCR values of these genes in strains JM101, PB11, PB12 and their rpoS − derivatives are shown in the included table. These RTPCR values have been previously reported [3], [11] and are presented in this figure for comparison and discussion purposes. The abbreviations are as follows: glucose (GLC), glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), fructose-6-phosphate (F6P), fructose-1,6-phosphate (F1,6P), dihydroxy-acetone phosphate (DHAP), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), glyceraldehyde-1,3-phosphate (G1,3P), 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG), 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), pyruvate (PYR), acetyl-CoA (AcCoA), acetyl phosphate (Ac-P), acetyl-AMP (A-AMP), citrate (CIT), isocitrate (ICT), glyoxalate (Gox), α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), succinyl-coenzyme A (SUC-CoA), succinate (SUC), fumarate (FUM), malate (MAL), oxaloacetate (OAA).