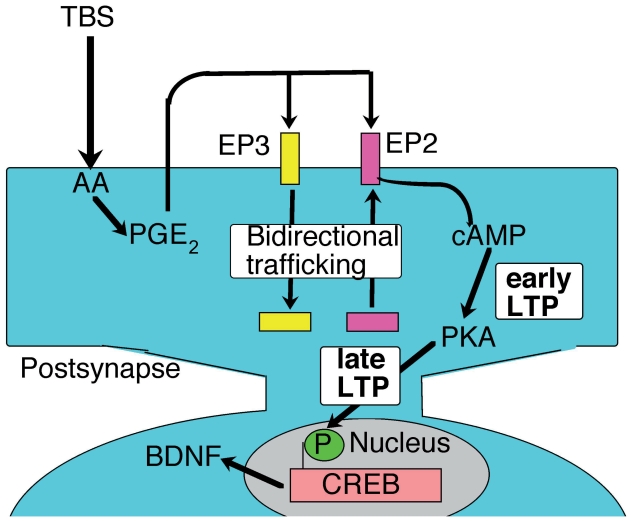
Figure 1.
Hypothetical mechanism of PGE2-mediated LTP in the visual cortex. TBS produces arachidonic acid (AA) from the membrane lipid substrate. AA is metabolized to PGH2 by COX-2 that has been activated concomitantly by TBS. PGH2 is converted immediately to PGE2 by PGE2 synthase. EP2 translocates from the cytosol to the membrane, simultaneously, with the translocation of EP3 from the membrane to the cytosol. The PGE2 that is generated spreads from postsynaptic sites into the synaptic cleft, where it activates EP2 at the postsynaptic membrane, resulting in the production of cAMP. Subsequently, cAMP activates PKA, which in turn activates CREB in the nucleus of postsynaptic cells in the visual cortex. This activation of CREB may induce the synthesis of proteins such as BDNF, which is involved in the L-LTP.