Fig. 5.
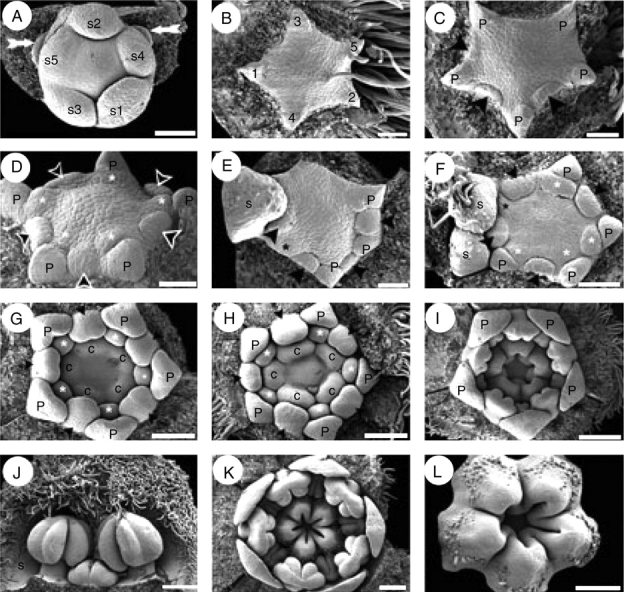
Quillaja saponaria, floral ontogeny. SEM micrographs. (A) Helical sepal initiation and two floral buds in the course of initiation (white arrows); subtending bracts of floral buds removed. (B) Helical initiation of petals indicated by numbers. (C) Unidirectional initiation of antesepalous stamen whorl (arrowheads) starting at the abaxial side; note that opposite stamen primordia do not develop simultaneously. (D) Floral bud after initiation of antesepalous stamens (black arrowheads) and antepetalous stamens (asterisks). (E) Hexamerous flower with unidirectional development of antesepalous stamen whorl (black arrowheads); adaxial petal primordium removed (upper side of the figure). Note the overlapping initiation of the last petal (black asterisk) and the stamens. (F) Floral bud with overlapping initiation of petals and stamens; adaxial petal (black asterisk) is underdeveloped with respect to stamens. Antesepalous (arrowheads) and antepetalous (white asterisks) stamen primordia are indicated; note that one abaxial antesepalous stamen is missing. (G) Independent and simultaneous initiation of carpels; antesepalous (black arrowheads) and antepetalous stamens (white asterisks) form two distinctive whorls. (H) Further development of gynoecium before lateral carpel fusion takes place. (I) Carpels start to fuse and form a continuous structure; the stamens are already differentiated into filament and anther. (J) Differentiated stamens from outer and inner androecium whorls; the outer members possess an enlarged filament. (K) Floral bud showing open gynoecium; ovule initiation is not evident at this stage, and petals remain distant from each other. (L) Carpels united at base and developing indumentum on their dorsal sides; ovules not yet evident. Abaxial floral side orientated to the bottom (A, C, E), to the right (F–I, K) and to the left (B). c, carpel; n, nectary; p, petal; s, sepal; s1–s5, order of initiation of sepal primordia. Scale bars: A, F = 100 µm; B–E = 50 µm; G, H, L = 150 µm; I, K = 200 µm; J = 250 µm.
