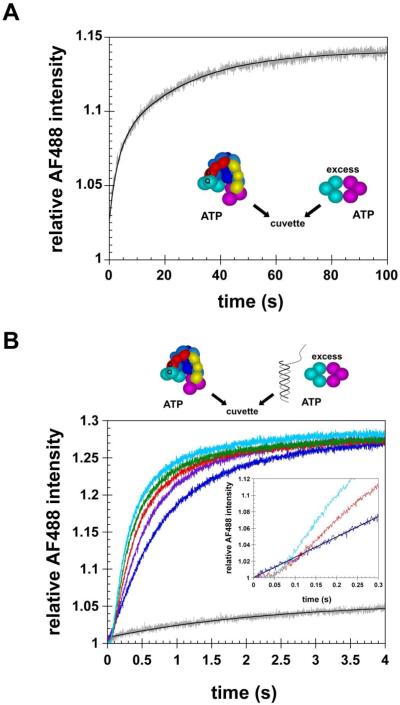
Figure 4. Passive dissociation of the clamp from the clamp loader versus active clamp loading onto DNA.
Dissociation of the clamp from the clamp loader was measured in two different experiments by adding a solution of γc-AF488, β-QSY9, and ATP to a solution of A) excess unlabeled β and ATP or B) p/t-DNA, excess unlabeled β, and ATP. Reactions in panel B contain 0 nM (gray trace), 25 nM (blue trace), 50 nM (purple trace), 100 nM (red trace), 200 nM (green trace), or 400 nM (cyan trace) p/t-DNA. Solid black lines through the gray traces containing no p/t-DNA in panels A and B are exponential fits of the data. Final concentrations were 20 nM γc-AF488, 400 nM β-QSY9, 8 μM unlabeled β, and 0.5 mM ATP in assay buffer containing 20 mM Tris·HCl pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, 8 mM MgCl2, and 4% glycerol.