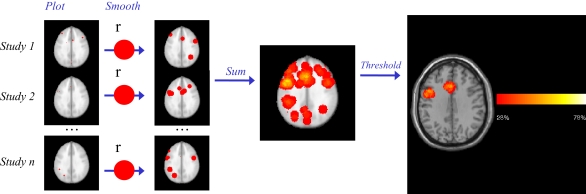
Figure 1.
Parametric Voxel-based Meta-analysis. Step 1: the coordinates for each study are plotted in standard space brain (MNI). Step 2: After smoothing with a uniform kernel of size r, each study map is transformed into an indicator map, where voxels with 1 values (red) indicate the presence of at least one activation within distance r. Step 3: all study-level indicator maps are summed and then divided by the number of studies n, to obtain a summary map reflecting the proportion of studies reporting an activation within distance r of each voxel. Step 4: the p value of the observed proportion is computed, under the null hypothesis that the activations are generated at random spatial locations. The final thresholded map reflects the areas where the proportion of studies reporting activation is too high to have been generated by such null random process alone. In this example of a meta-analysis of language production in healthy subjects, Broca's area and anterior cingulate are revealed as areas of significant activation (Costafreda et al., 2009a).