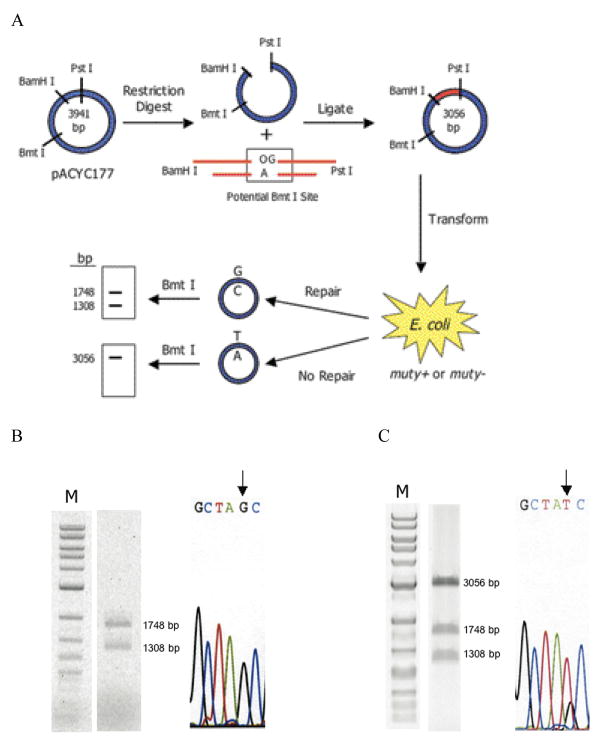
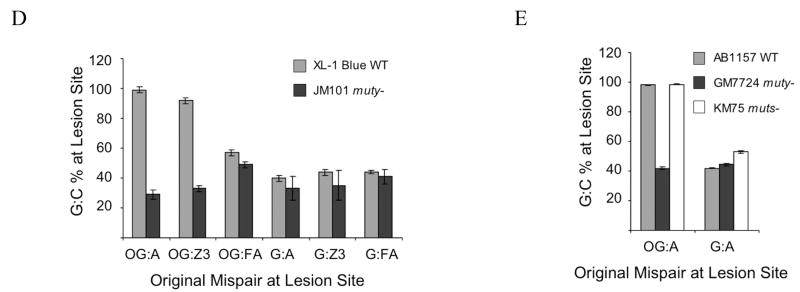
Figure 3. Cell-based MutY-mediated repair assay.
(a) Schematic representation of the assay. A mismatch-containing oligonucleotide is ligated into a plasmid vector and transformed into E. coli (mutY+ or mutY−). Repair or correct replication of the mismatch generates a G:C bp that creates a second Bmt I restriction site. The amount of G:C bp is determined via restriction fragment analysis of the recovered plasmid. The amount of repair mediated by MutY is determined by the % G:C bp created in cells containing MutY relative to those lacking MutY. (b and c) Restriction fragment and sequence analysis of lesion-containing plasmids rescued from E. coli. Representative data depicting initial plasmid containing an OG:A mismatch that has been completely converted to G:C (b). and initial plasmid containing a G:A mismatch that has not been converted completely to G:C (c). Gels shown are EtBr-stained agarose (M = 1 kb DNA ladder). Sequencing portion shown is of the BmtI recognition sequence and the arrow points to the location of the lesion. Levels of repair (percent G:C at lesion site) mediated by MutY are assessed by quantification of the agarose gels in which the percent G:C represents an average of at least three separate experiments in which > 100 colonies were pooled and amplified for the digestion analysis. (d and e) Summary graph of percent G:C bp determined from restriction fragment analysis of various base pair mismatches in E coli strains XL-1 Blue and JM101 mutY− (d) and AB1157, GM7724, and KM75 (e). Repair is related to the amount of G:C base pairs produced at the lesion site determined by BmtI restriction fragment analysis of mismatch-containing plasmid isolated from E. coli possessing MutY versus lacking MutY. Data represent mean values and error bars represent standard deviation of the sample set, which include at least three separate experiments.