Figure 5.
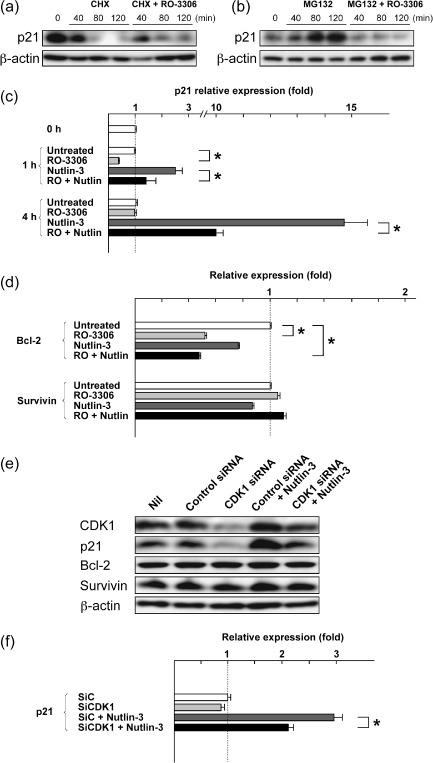
Cyclin‐dependent kinase (CDK) 1 inhibition prevents p53‐induced p21 synthesis. (a,b) MOLM‐13 cells were preincubated for 1 h with (a) 70 µM cycloheximide or (b) 0.2 µM MG132, and p21 levels after the addition of 5 µM RO‐3306 were monitored. Results are representative of three independent experiments. β‐Actin was used to confirm equal loading of proteins. (c) MOLM‐13 cells were treated with 5 µM RO‐3306 or 5 µM Nutlin‐3 for 4 h, either as individual agents or in combination, and p21 transcripts were quantitated by real‐time RT‐PCR. Each real‐time PCR was carried out in triplicate, and the average fold induction relative to time 0 is shown with SD. *Significance at P < 0.05. (d) MOLM‐13 cells were treated with 5 µM RO‐3306 or 5 µM Nutlin‐3 for 4 h, either as individual agents or in combination, and Bcl‐2 and survivin transcripts were quantitated by real‐time RT‐PCR. Each real‐time PCR was carried out in triplicate, and the average fold induction relative to untreated cells is shown with SD. *Significance at P < 0.05. (e) Western blot analysis of HCT116 cells transfected with either control or CDK1 siRNA. CDK1 siRNA led to reduced basal and p53‐induced p21 expression. (f) HCT116 cells were transfected with either control (SiC) or CDK1 siRNA (SiCDK1), and were incubated for 4 h in the absence or presence of 10 µM Nutlin‐3. p21 transcripts were quantitated by real‐time RT‐PCR. Each real‐time PCR was carried out in triplicate, and the average fold induction relative to untreated cells is shown with SD. *Significance at P < 0.05.
