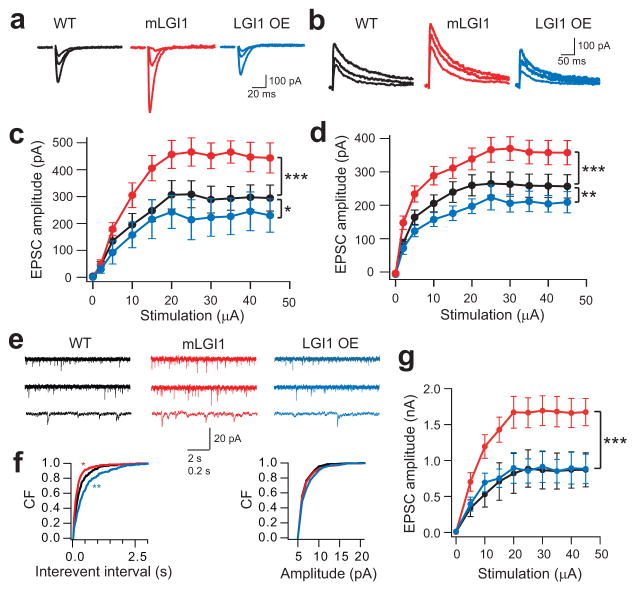
Figure 4.
ADLTE mutant LGI1 increases glutamatergic synaptic transmission. (a,b) Representative traces showing evoked AMPA (a) and NMDA (b) receptor-mediated EPSCs (2 μA, 5 μA, and saturating stimulus intensities) in wild-type (WT), mLGI1, and LGI1 OE mice. (c,d) Quantification of EPSC amplitude to stimulus intensity for AMPA (c, WT, black, n = 10; mLGI1, red, n = 7; LGI1 OE, blue, n = 6) and NMDA (d, WT, black, n = 11; mLGI1, red, n = 11; LGI1 OE, blue, n = 7) receptor currents. (e) Representative traces showing mEPSCs recorded from GCs of WT, mLGI1, and LGI1 OE transgenic mice. (f) Cumulative frequency plots of mEPSC interevent interval and amplitude for WT (black), mLGI1 (red), and LGI1 OE (blue) transgenic mice (n = 5). (g) Quantification of maximum evoked EPSC in DTX in WT (black symbol, n = 3), mLGI1 (red symbol, n = 4), and LGI1 OE (blue symbol, n = 3) mice. *:P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01; ***: P < 0.001.