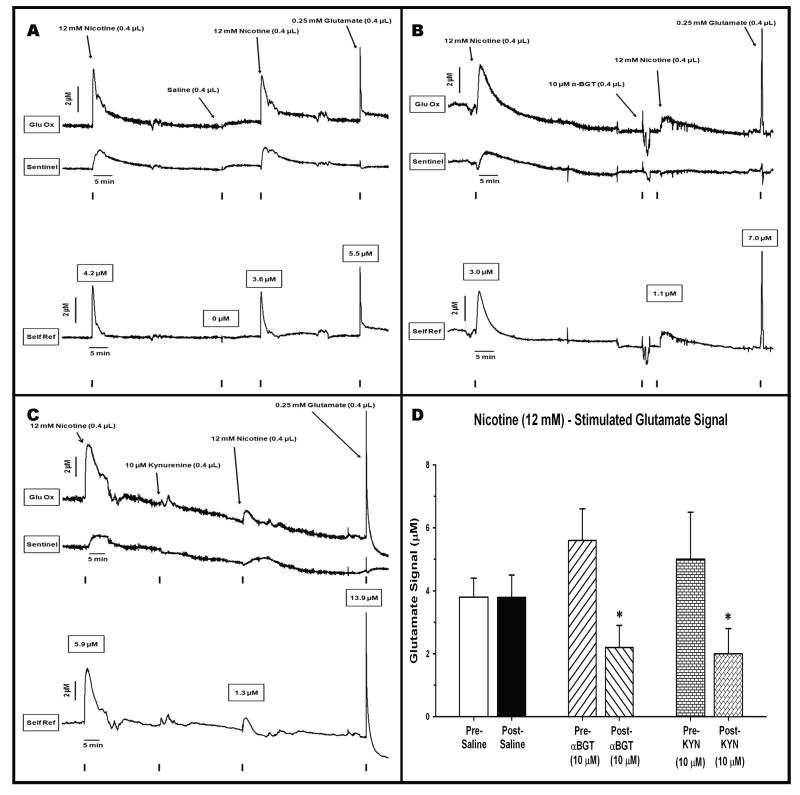
Figure 4.
Representative recordings from animals receiving intra-cortical infusions of nicotine separated by infusion of saline or α7nACh receptor antagonists. (A) effects of saline: The two infusions of nicotine (marked by TTLs on bottom of graph) produced similar signals on the Glu Ox site (top tracing) as well as increased the non-glutamatergic background signal (middle tracing). The infusion of saline was without effect on any channel. Self-referencing isolated the signal due to glutamate (bottom tracing). This signal rose rapidly to maximum amplitude and then was cleared more gradually. The nicotine-induced signal was similar to that seen following the infusion of an exogenous glutamate standard at the end of the test session. (B) effects of α-BGT: the bottom, self-referenced tracing reveals that the initial infusion of nicotine produced a clear increase (3.0 μM) in glutamate. Infusion of α-BGT, 5 min earlier, markedly attenuated the second nicotine-induced glutamate signal by 64% (1.1 μM). This attenuation did not reflect a loss in the ability of the MEA to detect glutamate as a control infusion of exogenous glutamate still produced a robust (7.0 μM) signal. (C) effects of kynurenine: the bottom self-referenced tracing shows that the initial infusion of nicotine produced a clear increase (5.9 μM) in glutamate. Infusion of kynurenine 40, min earlier, significantly attenuated the second nicotine-induced glutamate signal by 78% (1.3 μM). Kynurenine did not impair the MEA's ability to detect glutamate as the infusion of a glutamate control results in a marked elevation (13.9 μM) in the glutamate signal. (D) Group data: maximum amplitude (μM; mean ± S.E.M.) is depicted following two infusions of nicotine (12 mM in 0.4 μL). The nicotine infusions were conducted both before and after the administration of saline (control), α-BGT, or kynurenine. Separate groups of rats (n = 6/group) were tested in each nicotine-drug combination. * = amplitudes significantly reduced post- relative to pre-α-BGT (P = 0.008) or pre-kynurenine (P = 0.017).