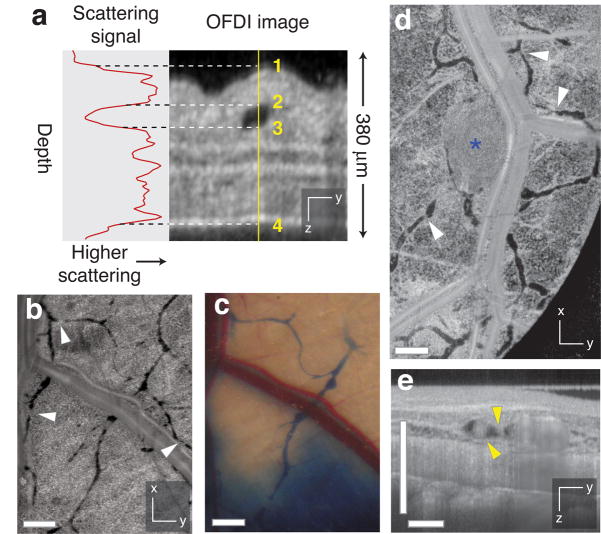
Figure 3.
Contrast-free lymphangiography using OFDI. (a) The scattering signal along a single depth scan within an OFDI image of a mouse ear shows the reduced scattering between the upper (2) and lower (3) boundaries of a patent lymphatic vessel. Scattering within the vessel is similar to background levels above the upper surface of the ear (1) or below the lower surface (4). (b,c) In addition to lymphatic vessels revealed by traditional cutaneous injection of Evan’s blue dye (c), OFDI was able to detect numerous additional vessels in the normal dorsal skin (b) and resolve the lymphatic valves found between individual lymphangions (white arrowhead,  ). (d) HSTS26T tumor (blue asterisk, *) associated lymphatics exhibiting hyperplasia. (e) Cross-sectional presentations of a lymphatic vessel showing cellular masses (yellow arrowhead,
). (d) HSTS26T tumor (blue asterisk, *) associated lymphatics exhibiting hyperplasia. (e) Cross-sectional presentations of a lymphatic vessel showing cellular masses (yellow arrowhead,  ) located near the tumor in d. Scale bars, 500 μm.
) located near the tumor in d. Scale bars, 500 μm.