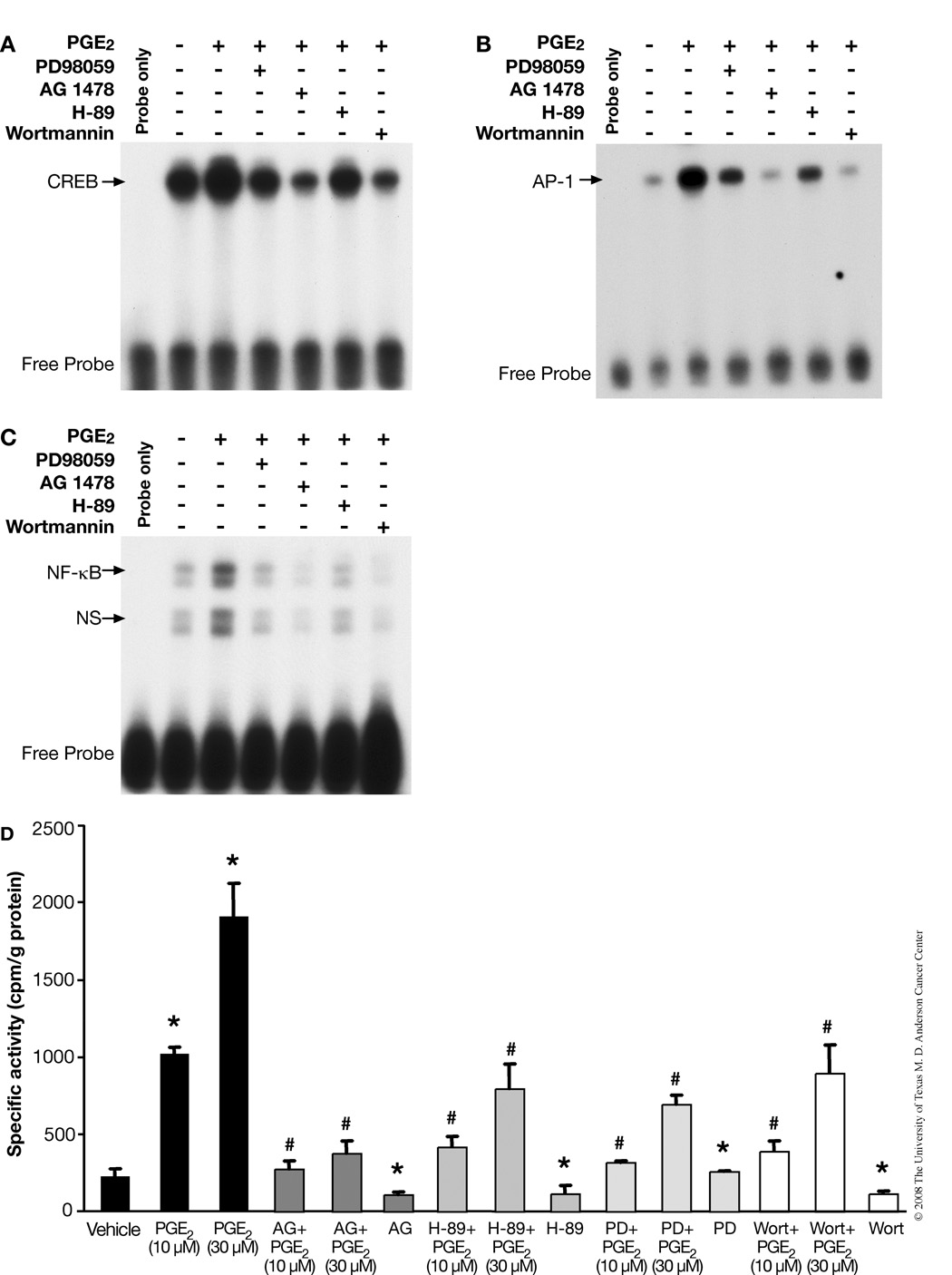
FIGURE 3.
PGE2-induces activation of CREB, AP-1 and NF-κB transcription factors in PMKs. PMKs were incubated with vehicle (control, lane 2) or with PGE2 (10 µM) (lanes 3–7) for 15 min. To demonstrate the effect of phamacological inhibitors on PGE2-induced transcription factor-binding, PMKs were treated with PD98059, AG1478, H-89 or wortmannin for 30 min prior to PGE2 treatment. Nuclear extracts were subjected to electrophoretic mobility shift assay analysis, as described in experimental procedures. A. PGE2-induced CREB activation in PMKs. The arrow indicates the specific binding of CREB to its consensus oligonucleotide. B. PGE2-induced AP-1 activation in PMKs. The arrow indicates the specific binding of AP-1 to its consensus oligonucleotide. C. PGE2-induced NF-κB activation in PMKs. The arrows indicate the specific binding of NF-κB to its consensus oligonucleotide (upper arrow) and non-specific (ns) binding (lower arrow). D. EGFR, ERK1/2, PKA/CREB and PI3-K/Akt signaling cascades are involved in PGE2-stimulated cell proliferation. PMKs were treated with various kinase inhibitors 30 min prior to PGE2 (10 µM) treatment for 20 h and pulsed with (3H)-thymidine 2 h before harvest. The (3H)-thymidine incorporated by PMKs was measured in triplicate samples and normalized to protein concentration as described in experimental procedures. Representative data from at least 2 independent experiments are presented as the means ± SD. *p<0.05, significant when compared to vehicle-treated groups and #p<0.05, significant when compared to PGE2-treated groups.