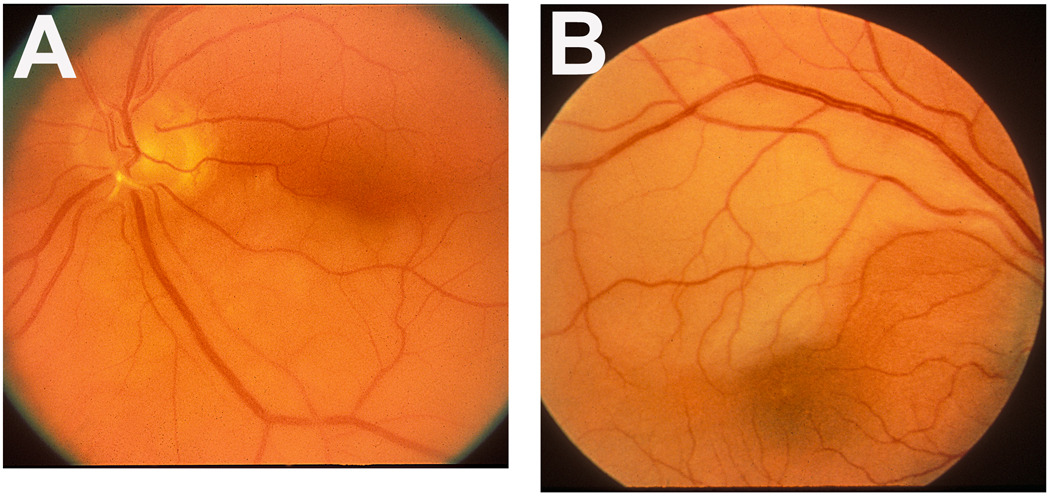
Figure 4.
Fundus photographs of two eyes with branch retinal artery occlusion.
A: Left eye with inferior branch retinal artery occlusion, with an embolus (white) impacted at its origin on the optic disc. Note the junction between the normal (upper half) and infarcted (lower half) retina lies in the foveal region.
B: Right eye with superior temporal branch retinal artery occlusion. Note the junction between the normal (lower) and infarcted (upper) retina lies in the foveal region.