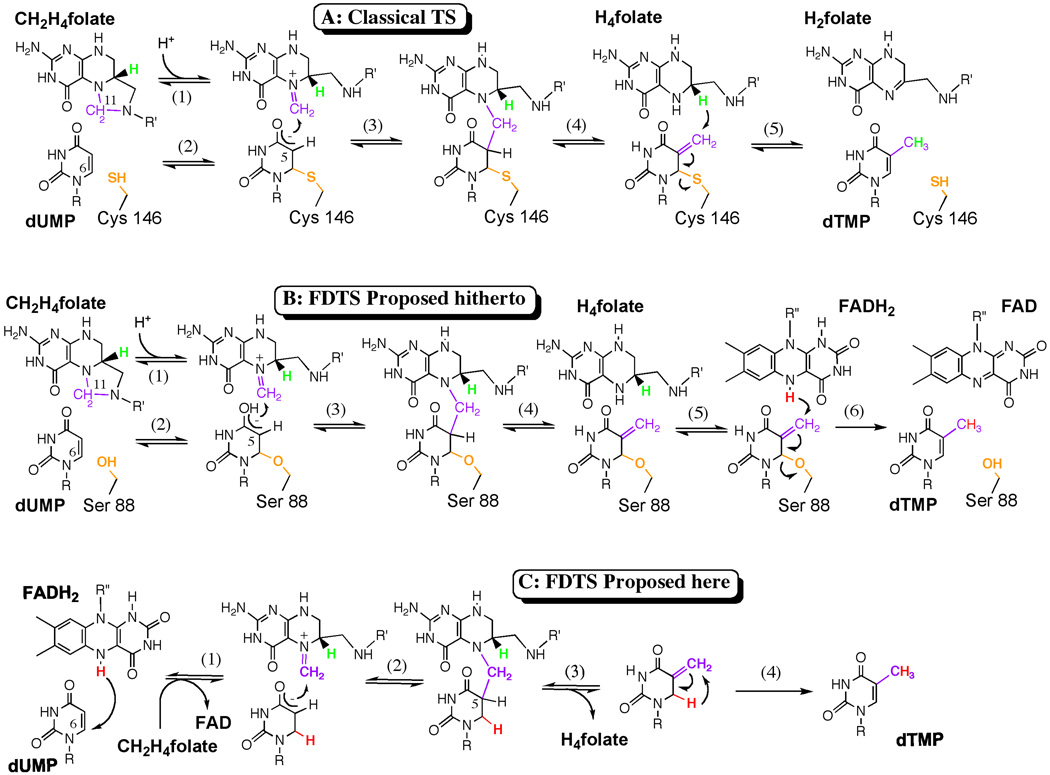
Figure 1. TSase mechanisms.
A. The chemical mechanism for the classical TS catalyzed reaction 1, 2. B. The chemical mechanism for the FDTS proposed hitherto 12. C. The newly proposed mechanism for the FDTS that does not rely on an enzymatic nucleophile. The conserved enzymatic nucleophile is orange, the methylene is purple, the reducing hydride from H4folate is green, and the hydride from FADH2 is red. R= 2’-deoxyribose-5’-phosphate and R’= (p-aminobenzoyl)-glutamate. R”= adenosine-5’-pyroposphate-ribityl.