Figure 9.
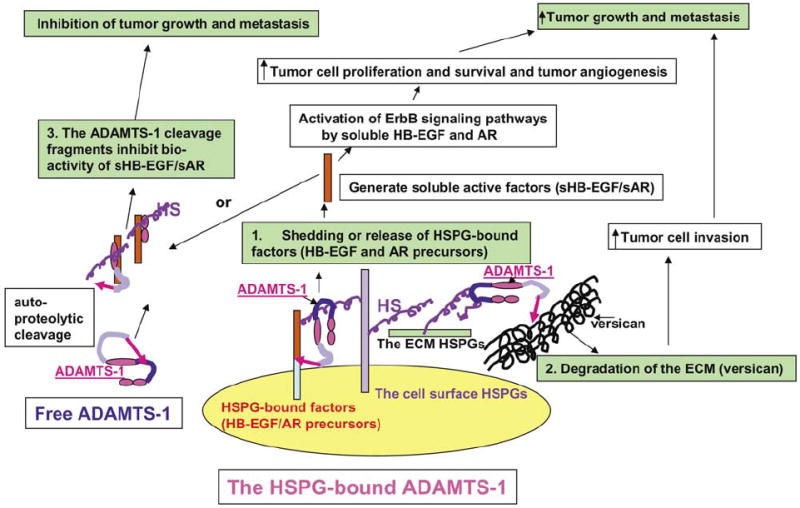
Model showing the potential mechanisms underlying the opposite effects of ADAMTS-1 and the ADAMTS-1 fragments on tumor metastasis. We propose that full-length ADAMTS-1 promotes tumor metastasis by stimulating tumor cell proliferation/survival/invasion and tumor angiogenesis through shedding/activation of the HSPG-bound factors, including HB-EGF and AR transmembrane precursors. We further postulate that this process requires the metalloproteinase activity of ADAMTS-1, and that full-length ADAMTS-1 binds to its substrates through its spacer/Cys-rich domain. In addition, we propose that the antitumor activity in the ADAMTS-1 fragments, ADAMTS-1NTF and ADAMTS-1CTF, resides in the TSP-1 domains, which exert the antitumor activity by inhibiting the bioactivity of several soluble heparin-binding growth/angiogenic factors, including AR, HB-EGF, and VEGF.
