Figure 4. Lnx-l counteracts Boz-mediated dorsalization.
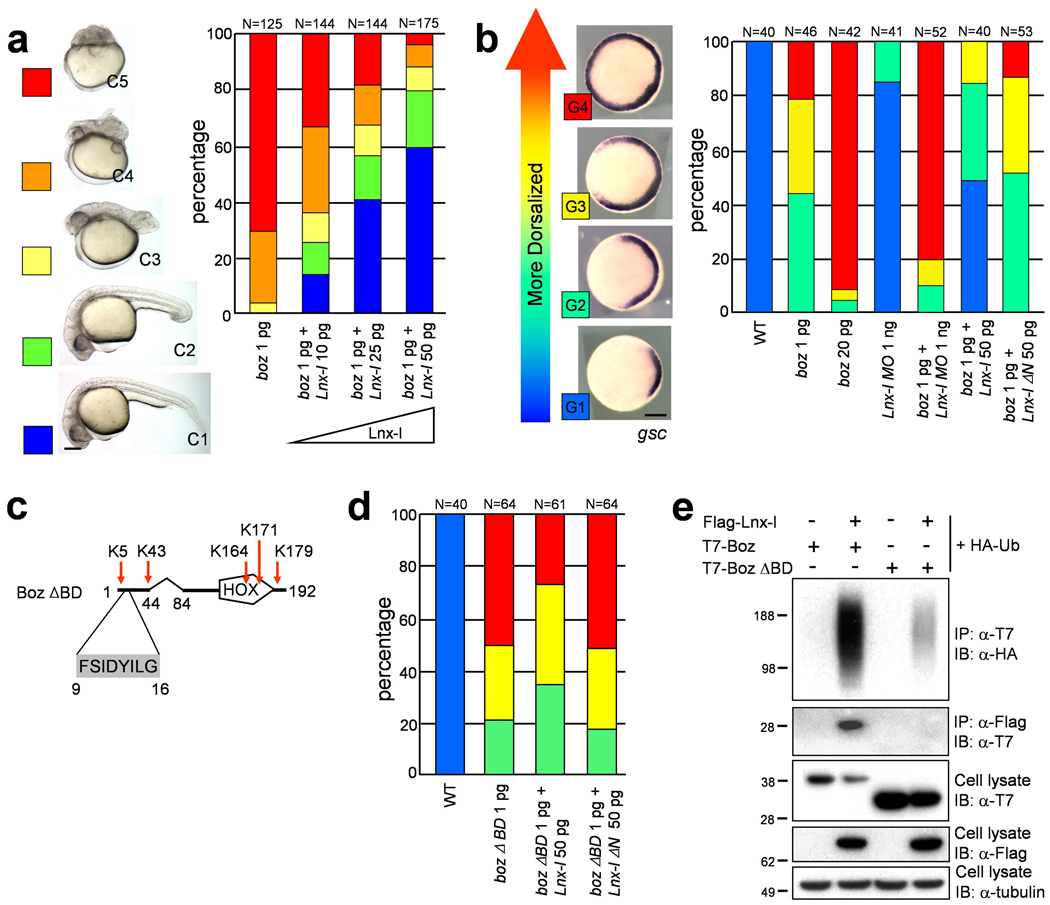
a, b, d, The amounts of injected RNA or MO are shown beneath each bar, and number of embryos above each bar. a, Coinjection of lnx-l mRNA rescues boz-induced dorsalization. The embryonic morphology was classified as C1-C5 at 26 hpf, as illustrated at the left. b, Dorsalization was analyzed by observing the domain of gsc expression at the germ ring stage. Boz and lnx-l MO show synergism, while lnx-l mRNA counteracts dorsalization. c, Schematic drawing of Boz lacking the Lnx-l binding domain (Boz ΔBD), but retaining the Goosecoid-Engrailed homology domain (amino acid 9–16) and all lysine residues. d The gsc expression level, analyzed as in b, shows that Boz ΔBD is resistant to Lnx-l (compare to b). e, T7 epitope-tagged Wt Boz or Boz ΔBD was cotransfected into 293T cells with Flag-Lnx-l and HA-Ub. Boz ΔBD ubiquitination is almost absent. Scale bar, 200 µm.
