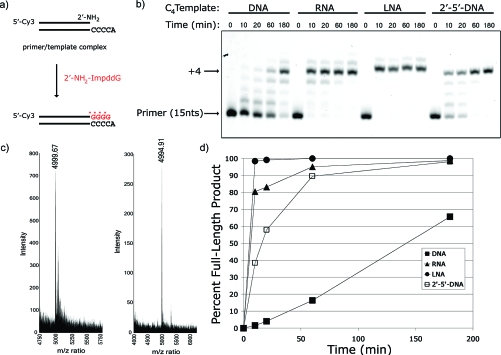
Figure 2.
Primer-extension reaction using a 2′-NH2−ImpddG as monomer. (a) Primer-extension reaction scheme showing a 5′-Cy3-labeled 2′-amino-terminated DNA primer annealed to a complementary template. 2′-NH2−ImpddG monomer participates in a chemical chain reaction extending the primer by four (4) nucleotides on the complementary template forming a N2′→P5′-DNA polymer product. * indicates new phosphoramidate bond. (b) High-resolution gel electrophoresis analysis of primer-extension products on indicated templates. Primer-extension reactions contained 0.1 μM Cy3-labeled-2′-amino-terminated DNA primer, 0.5 μM template, 100 mM MES-CAPS-HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM 1-(2-hydroxyethyl)imidazole, and 5 mM 2′-NH2−ImpddG. The reaction was initiated by addition of 2′-NH2−ImpddG, thermal cycling as described in the , and incubation at 4 °C for the indicated time. Arrows indicate primer and full-length product. (c) MALDI-TOF MS analysis of primer-extension product. 100−200 pmol amino-terminated primer was extended on an RNA template followed by base hydrolysis of the RNA template and preparation for MALDI-TOF MS as detailed in the . DNA control oligonucleotide (left): calcd mass 4999.87 and observed mass 4999.67; N2′→P5′-DNA extension product (right): calcd mass 4994.95 and observed mass 4994.91. (d) Graphical summary of primer-extension reactions. Primer-extension reaction efficiency is expressed as percent full-length product (≥+4) achieved at the given time point.