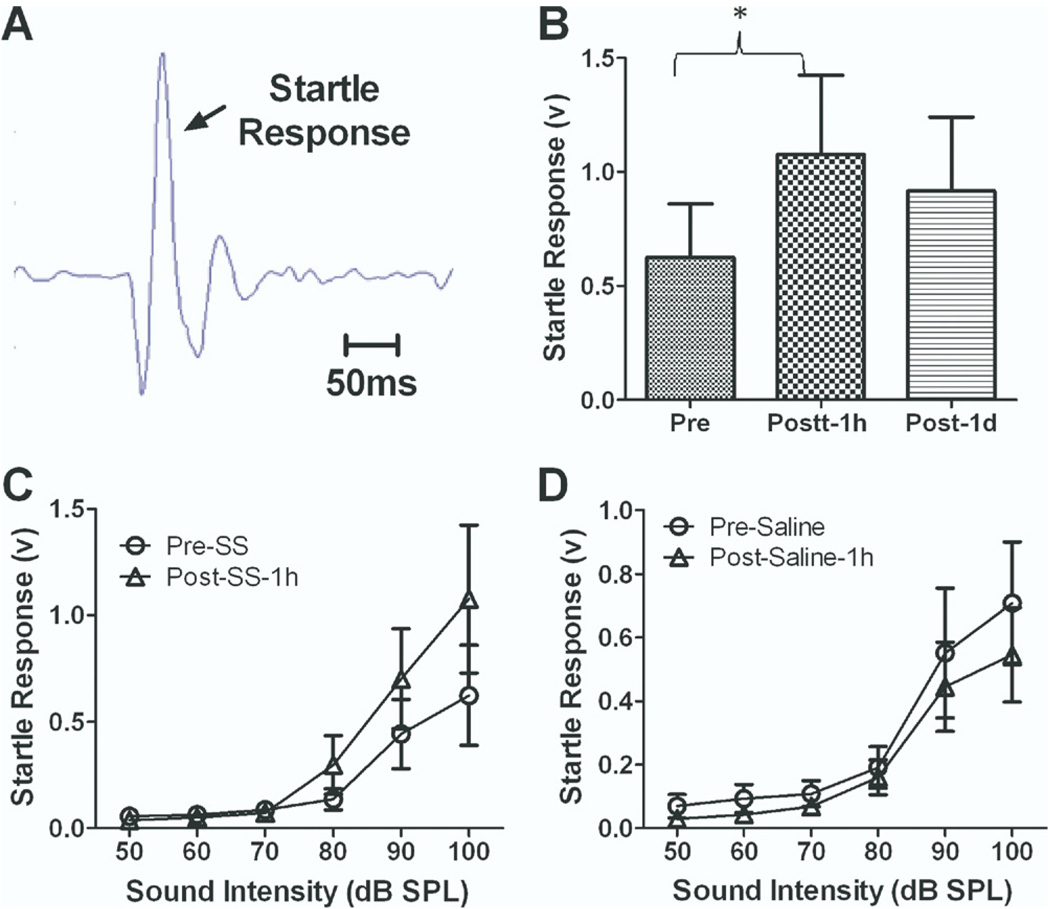
Fig. 6.
Salicylate (250 mg/kg i.p.) injection induced an enhancement of the acoustic startle response. (A) A typical startle response recorded from a rat. (B) The amplitude of the acoustic startle response evoked by 100 dB SPL sound stimuli significantly increased 1 h after the salicylate injection and partially recovered on the second day. (C) The average startle amplitude evoked by sound stimuli from 50 to 100 dB SPL recorded before and 1 h after salicylate injection. One hour after salicylate injection, startle amplitude at high sound intensity (70–100 dB SPL) increased significantly. (D) Startle amplitude recorded before and 1 h after saline injection. The startle amplitude showed a slight decrease 1 h after saline injection.