Figure 11.
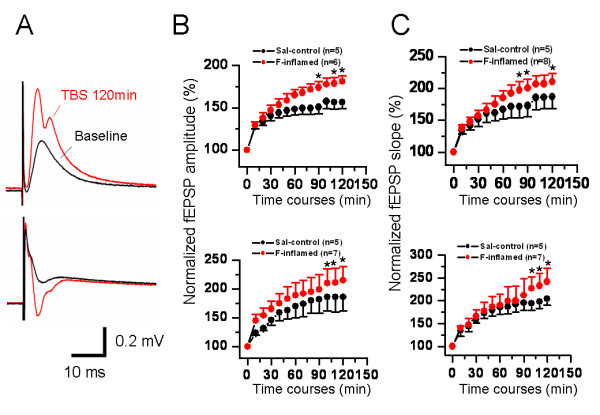
Showing a comparison of long-term potentiation (LTP) of field excitatory postsynaptic potential (fEPSP) in the hippocampal formation induced by perforant path theta burst stimulation (TBS) conditioning between groups of rats in saline (Sal-control) and formalin (F)-inflamed state. A, a typical example of F-induced alteration in the shape of fEPSP at 120 min after TBS. The amplitude (B) and slope (C) of both dentate gyrus (upper) and CA1 (lower) fEPSP were normalized as percentage of the pre-TBS baseline and plotted as a function of time. F-evoked persistent pain could also produce enhancement of LTP in hippocampal slices. The number of slices used to plot the graph is indicated in parentheses. *P < 0.05 vs. saline control. Error bars: ± S.E.M.
