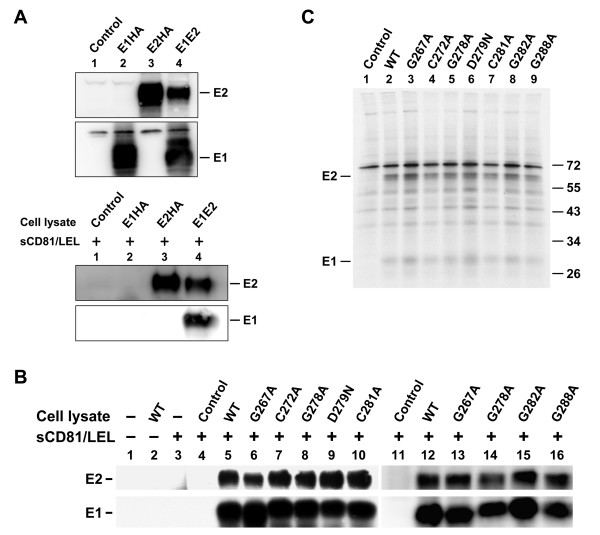
Figure 4.
Analysis of the CD81-binding ability of E2 and of the E1-E2 interactions in mutant proteins. (A) 293T cells were transfected with pcDNA3 (marked as the control), pHCMV-E1HA, pHCMV-E2HA, and WT pcDNA3-E1E2 plasmids, respectively. Two days after transfection, cells were lysed with buffer containing 1% CHAPSO. A portion of the cell lysates was directly resolved by reducing SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using E1 and E2 MAbs, respectively (top panel). Another portion of the lysates was incubated with equal volumes of concentrated sCD81-LEL followed by incubation with protein A-Sepharose beads. The precipitated proteins were resolved by reducing SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using E2 and E1 MAbs, respectively (bottom panel). (B) 293T cells were transfected with pcDNA3 (marked as the control) or with each of the WT and mutant E1E2 plasmids. Two days after transfection, cell lysates were incubated with or without concentrated sCD81-LEL followed by incubation with protein A-Sepharose beads. The isolated proteins were resolved by reducing SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using E2 and E1 MAbs, respectively. (C) Coprecipitation of E1 and E2 with a conformation-dependent E2 MAb H53. 293T cells were transfected with pcDNA3 (marked as the control), WT, or mutant E1E2 plasmids. Transfected cells were metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine for 30 min and chased for 4 h. Cell lysates were successively incubated with the H53 MAb and protein-A-Sepharose beads, and the isolated proteins were subjected to nonreducing SDS-PAGE followed by fluorography.