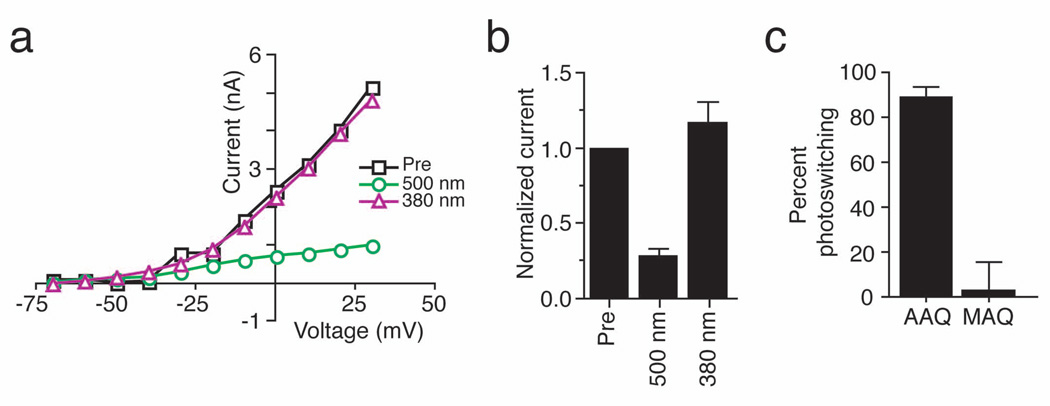
Figure 3. Photocontrol of native K+ current in cultured hippocampal neurons.
(a) Steady-state I–V curves from a voltage-clamped hippocampal pyramidal neuron before (Pre; black squares) and after a 15 min application of 300 µM AAQ. Photoisomerization of AAQ to the trans state with 500 nm light (green circles) reduces voltage-gated K+ current whereas illumination with 380 nm light (violet triangles) restores current to levels similar to those measured prior to AAQ treatment.
(b) AAQ-treated channels are completely unblocked by 380 nm light. Voltage-gated currents (elicited by stepping from −70mV to +30mV) measured after AAQ treatment were normalized to those measured prior to AAQ application (n = 5).
(c) Percent photoswitching for K+ current in hippocampal neurons treated with AAQ (200 µM) or MAQ (250 µM) (n = 6 for each). Light has no effect on the steady-state I–V curve from a non-transfected neuron treated with MAQ. MAQ only imparts light-sensitivity on neurons transfected with the Shaker E422C channel10.