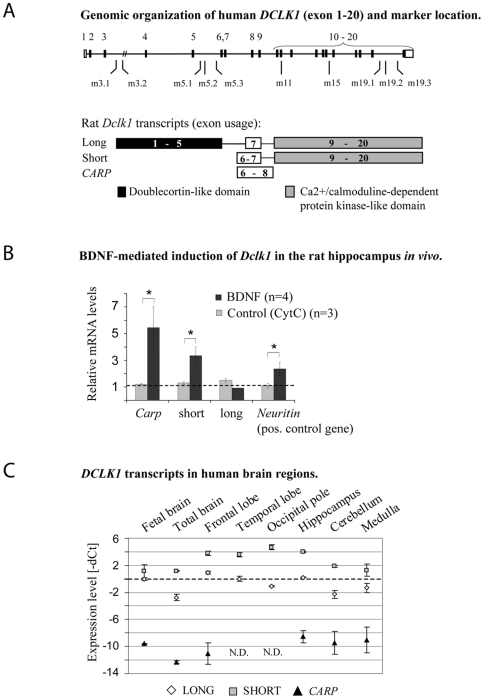
Figure 1. Genomic organization of human DCLK1 and expression of transcript variants in human brain regions and in rat hippocampus in response to BDNF.
(A) Proposed genomic organization, exon usage and marker location for the human DCLK1 gene. In rodents, Dclk1 contains 20 exons producing several transcripts, such as long, short and Carp mRNAs. In human, the reference sequence only lists 18 exons encoding the long DCLK1 transcript (NM_004734). With transcript-specific RT-PCR assays (see below, panel C), we show that short DCLK1 and CARP are expressed in humans (with inclusion of exon 6 and 8), thus the human genomic sequence should contain 20 exons. Black, white and grey boxes illustrate protein domains encoded by different exons. The genomic locations of markers with positive scores or interactions are marked. (B) The expression of Dclk1 variants in response to infusion of exogenous BDNF into the dentate gyrus in vivo were analyzed by real-time RT PCR. BDNF mediates the expression of short Dclk1 variants and Carp, while the long (full-length) Dclk1 transcripts are unaffected (or slightly reduced). Infusion of Cytochrome C was used as a negative control. (C) RT-PCR amplification of N-terminal- (“long”) and C-terminal (“short”) domain DCLK1 transcripts and CARP expressed in human brain regions. –dCt values are given relative to the Ct of long DCLK1 in fetal brain (dotted line, Ct = 22.9, mean ± S.E.M.). N.D.: not detected / variable detection.