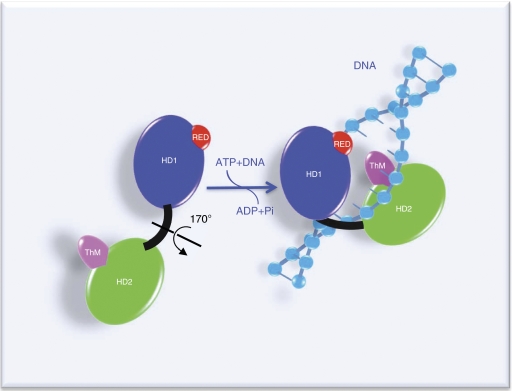
Figure 7.
Proposed structure-based mechanism for binding of XPB to DNA. In this model, adapted from Fan et al (2006), XPB is in an opened conformation in the absence of DNA. When XPB binds to DNA, the rotation (170°) of the second helicase domain (HD2) together with the ThM domain, facilitated by HD1-mediated ATP hydrolysis, forms the closed and stable XPB–DNA complex.