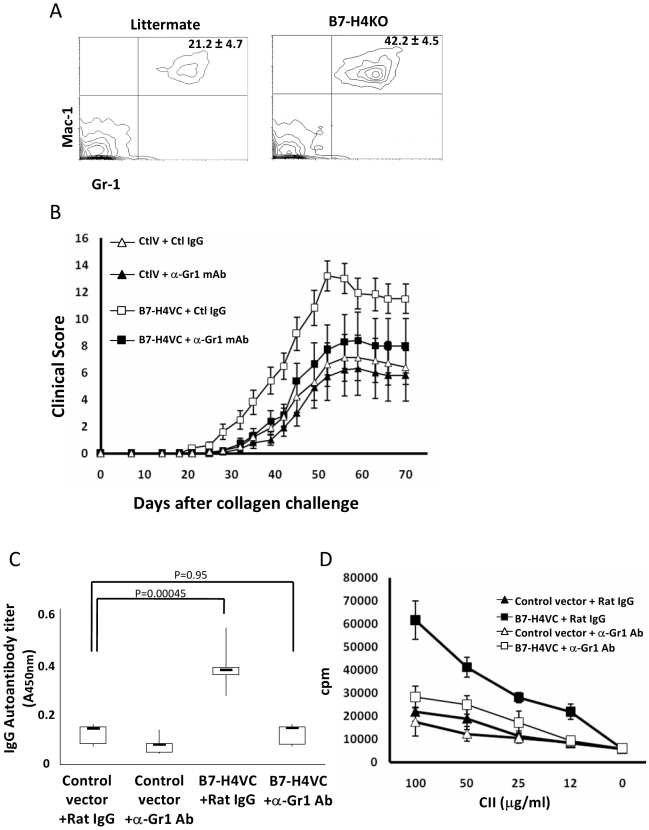
Figure 4. Gr-1+ cells are required for sH4-mediated exacerbation of CIA.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of peripheral blood from the B7-H4KO or littermates on Day 2 after being immunized with collagen in CFA. The percentages of Gr-1+ Mac-1+ cells are shown and the results are presented as means±standard deviation (n = 5). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (B) Depletion of Gr-1+ neutrophil ameliorates sH4-induced exacerbation of CIA. Mice were treated with either control (ctlV) or B7-H4VC plasmids (B7-H4VC) at day −1 and 14 of collagen immunization to induce CIA. To deplete Gr-1+ cells, mice were injected i.p. with 0.3 mg of anti-Gr-1 mAb (clone RB6-8C5) or control rat IgG every other day starting at day −1 of CIA induction and stopping at day 14. Each point represents results from a pool of ten mice and the bars are means ± 95% confidence interval. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by repeated ANOVA method (p<0.0001). The following Tukey-Kramer test showed significant difference at each point after Day 28 between the B7-H4VC+ Ctl IgG group and other three groups (p<0.01). (C) Depletion of Gr-1+ cells inhibited sH4-mediated production of autoantibodies to collagen. CIA mice were treated with indicated plasmids and anti-Gr-1 antibody as described in (B). Sera were sampled on day 30 after collagen immunization. Serum anti-collagen IgG level was determined by specific ELISA as described in Materials and Methods. Each group represents results from a pool of five mice. The top and bottom of each rectangular box denote the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively, with the median shown inside the box. Error bars extending from each box represent the maximum and minimum. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA method followed by the Scheffé test. (D) Depletion of Gr-1+ cells inhibited sH4-mediated proliferation of splenocytes to CII. CIA mice were treated with indicated plasmids and anti-Gr-1 antibody as described in (B). Whole splenocytes from the mice at day 30 after collagen immunization were cultured in the presence of the indicated concentrations of CII for 72 h. The cultures were pulsed with 3HTdR 18 h before harvest and cpm were counted by a scintillation counter. Each point represents results from three wells and data represent five independent experiments and are expressed as means ± 95% confidence interval.