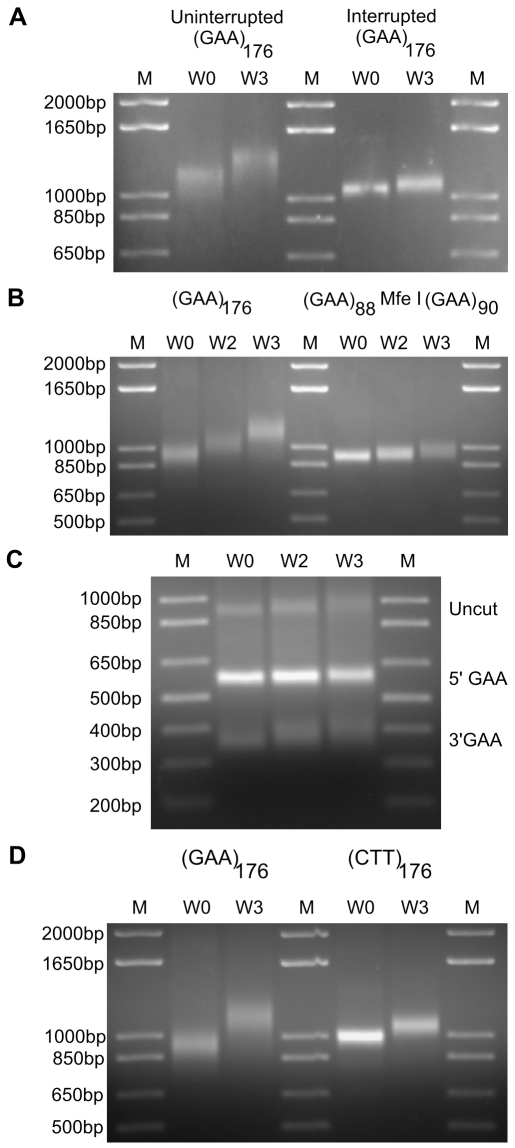
Figure 3. Expansion levels are affected by the purity of the repeat sequence and the repeat orientation.
(A) PCR analysis of GAA·TTC expansion within an uninterrupted (GAA·TTC)176 insert at W0 and W3 compared to a (GAA·TTC)176 insert with two interrupting mutations identified by sequencing analysis. An A→T mutation was detected approximately 118 triplets into the repeat region from the 5′ end and a T→G mutation was detected 31 triplets into the repeat region from the 3′ end. PCR amplification adds 438 bp to the GAA·TTC insert. M: 1 Kb plus size standard. (B) PCR analysis of GAA·TTC expansion within an uninterrupted (GAA·TTC)176 insert at W0, W2, and W3 compared to a (GAA·TTC)88MfeI(GAA·TTC)90 insert sequence containing an interrupting hexamer sequence located between two repeat tracts. The CAATTG hexamer is the recognition sequence for the Mfe I restriction endonuclease. PCR amplification adds 438 bp to the GAA·TTC insert. M: 1 Kb plus size standard. (C) Mfe I digestion of the PCR amplification products from the (GAA·TTC)88MfeI(GAA·TTC)90 time-course at W0, W2, and W3. PCR amplification adds 338 bp to the 5′ end of the GAA·TTC insert and 100 bp to the 3′ end. Mfe I digestion yields two distinct fragments representing the promoter proximal (GAA·TTC)88 repeat tract (5′ GAA) and the distal (GAA·TTC)90 repeat tract (3′ GAA). The residual full-length product (Uncut) is due to incomplete digestion. M: 1 Kb plus size standard. (D) PCR sizing analysis of a (GAA·TTC)176 insert at W0 and W3 compared to a reverse oriented (CTT·AAG)176 insert sequence at the same time-points. PCR amplification adds 438 bp to the repeat insert. M: 1 Kb plus size standard. A representative gel from an n = 2 is shown.