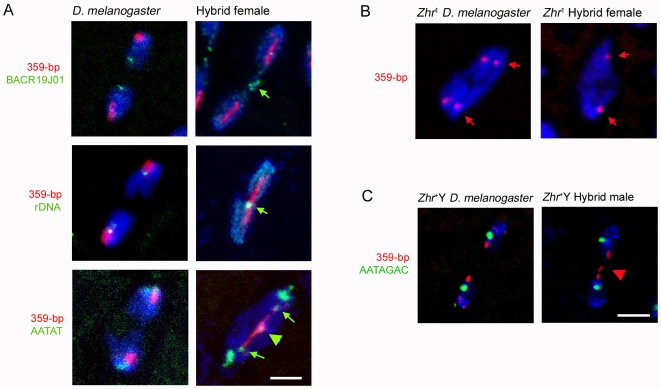
Figure 3. Stretched and lagging X heterochromatin is induced by sequences in the 359-bp satellite block in hybrid female embryos.
(A) Green arrows in right top and middle panels indicate unstretched euchromatin and rDNA, respectively. In the right bottom panel, green arrows highlight AATAT satellite DNA proximal to the 359-bp DNA block that is segregating to the spindle poles, while the green arrowhead indicates a small amount of stretched and lagging AATAT DNA. (B) Normal X chromosome segregation in hybrid females carrying the Zhr 1 compound-XY chromosome, which is devoid of the X-linked 359-bp satellite. The related satellites (353-bp, 356-bp, and 361-bp repeats, indicated by red arrows) on Chromosome 3 segregate normally. (C) 359-bp DNA translocated to the Y chromosome is stretched and lagging in a hybrid male embryo (right panel). The D. melanogaster control embryo carries the Zhr 1 compound-XY chromosome instead of a wild-type X chromosome, so that the only source of 359-bp satellite is the Y. The red arrowhead points to lagging Y-linked 359-bp satellite DNA. DNA is blue in all panels. Scale bar is 5 µm in (A) and 7 µm in (C).