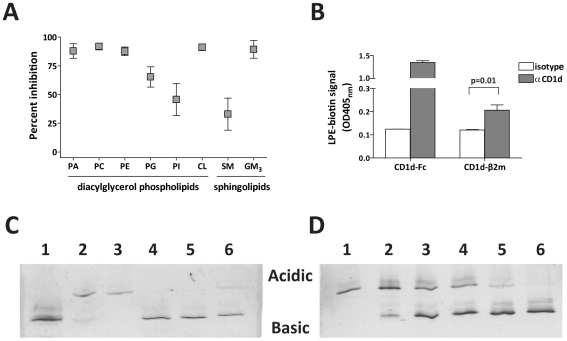
Figure 5. Effect of bound lipids on CD1d antigen loading.
(A) Immobilized CD1d molecules were preincubated with the indicated lipids or treated with vehicle alone for 24 h. Unbound lipids were washed away, and the CD1d molecules were incubated with the α-GSL C20:2 for 24 h, then tested for the ability to stimulate NKT cell cytokine secretion. Percent inhibition was calculated by comparing NKT cell cytokine secretion in response to C20:2 pulsed onto CD1d molecules pretreated with lipid compared to CD1d pretreated with vehicle alone. The plot shows means and standard deviations of results compiled from seven independent experiments. (B) Biotinylated LPE (15 µM) was incubated with CD1d-Fc fusion protein or with secreted CD1d-β2m heterodimers that contain a mixture of bound ligands [25]. The samples were then incubated on plates coated with an anti-CD1d mAb (filled bars) or with an isotype-matched negative control mAb (open bars), and bound LPE was detected using a streptavidin-enzyme conjugate. OD450nm, optical density at 450 nm. (C) Native isoelectric focusing (IEF) analysis of lyso-phospholipid binding to recombinant CD1d molecules. Purified native CD1d molecules were mock-treated (lane 1), or preloaded with the trisialoganglioside GT1b (lanes 2–6), then incubated in solution with free lipids and separated by electrophoresis according to charge. Lane 3 shows GT1b-CD1d incubated with additional GT1b; lane 4 shows GT1b-CD1d incubated with a 4.5-fold molar excess of α-GalCer; lane 5 shows GT1b-CD1d incubated with a 3-fold molar excess of LPC; and lane 6 shows GT1b-CD1d incubated with a 3-fold molar excess of LPE. (D) Titration of the amount of lyso-phospholipid required to displace bound GT1b. Lane 1 shows GT1b-CD1d incubated in buffer with no LPE; lanes 2–6 show GT1b-CD1d incubated with the following molar ratios of LPE: lane 2 = 1∶1, lane 3 = 1∶2, lane 4 = 1∶3, lane 5 = 1∶5, and lane 6 = 1∶9.