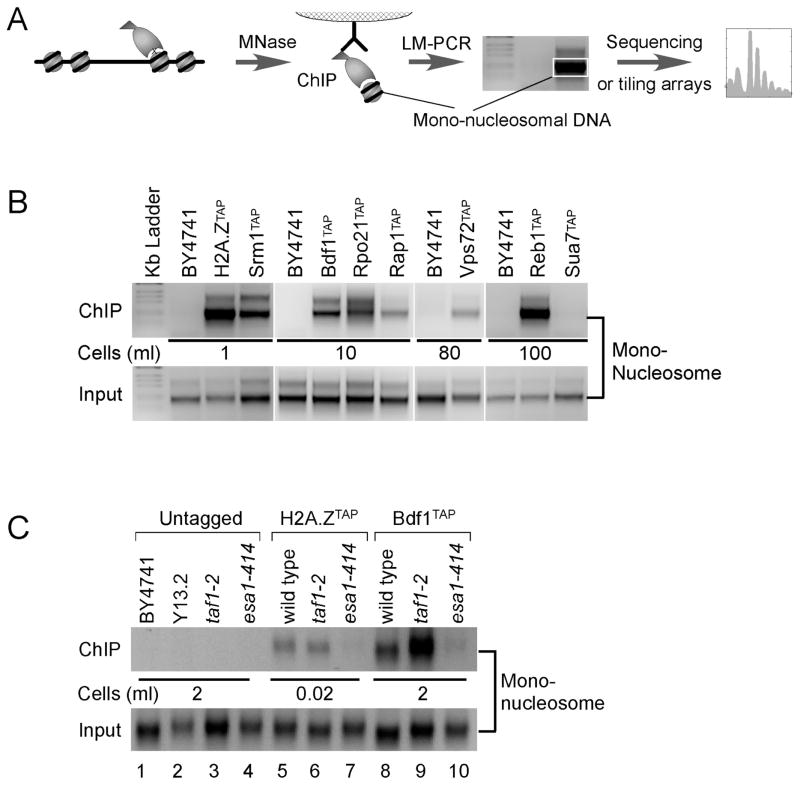
Figure 1. Identification of Factor-nucleosome Interactions in vivo.
(A) Diagram outlining the factor-nucleosome interaction assay. Cells encoding a TAP-tagged protein are treated with formaldehyde. Chromatin is then isolated and solubilized to mononucleosomes with MNase, then subjected to TAP purification. Adapter capture of mono-nucleosomal DNA produces an ~200 bp LM-PCR product, which can be subsequently mapped genome-wide.
(B) LM-PCR detection of the indicated factor-nucleosome interaction. BY4741 is a negative control that lacks the TAP tag; H2A.Z is a positive control. Input represents the equivalent of 10−5 ml of cell culture used in LM-PCR, and is the material used for the immunoprecipitation. The volume of cell culture (at OD600 = 0.8) used in the TAP purification is indicated.
(C) Bdf1-nucleosome interactions are dependent on Nua4 (Esa1)-directed acetylation. LM-PCR experiments were performed on the indicated strains as described in panels A and B.