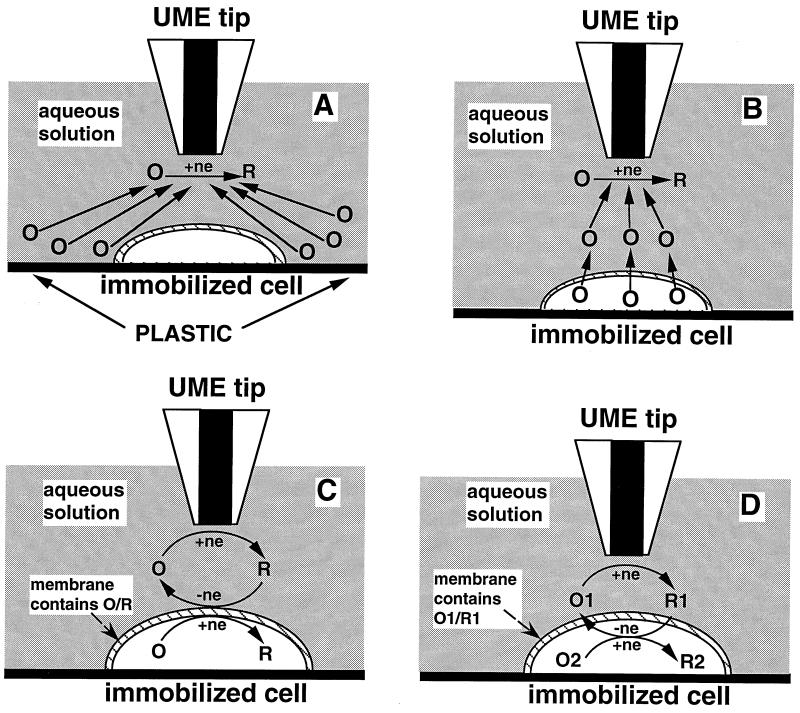
Figure 2.
Schematic diagrams of the SECM experiments with four different types of mediator regeneration. (A) The tip is positioned in the solution close to the cell surface. The lipid cell membrane is impermeable for a hydrophilic redox mediator. Negative feedback is due to the hindered diffusion of redox species to the tip electrode. (B) The UME tip induces the ejection of the redox species, O, from the cell by depleting its concentration near the cell surface via electrolysis. (C) Mediator regeneration proceeds via self-exchange ET reaction. The charge is shuttled across the membrane by the same hydrophobic redox species (O/R). (D) Bimolecular ET between hydrophobic redox mediator (O1/R1) and cell-bound redox moieties (O2/R2).