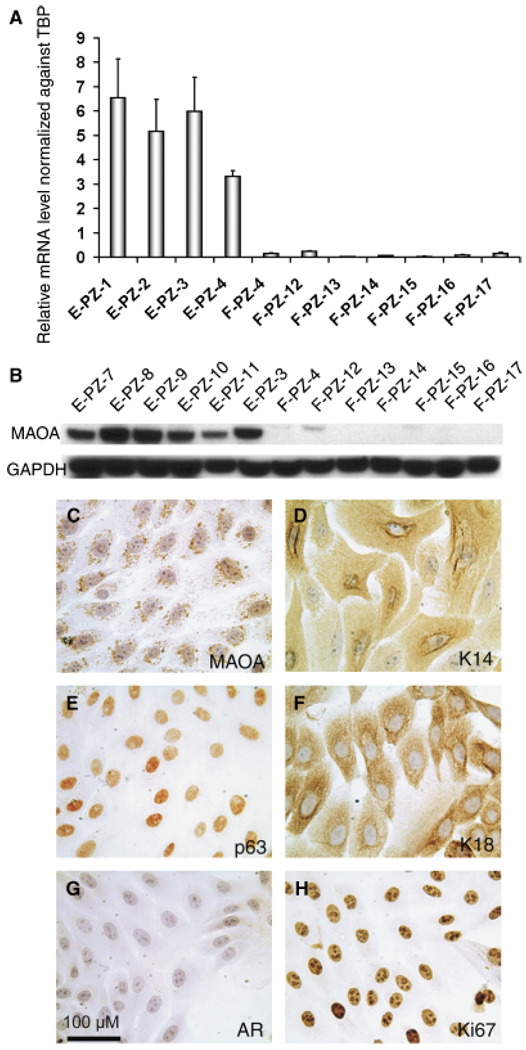
Fig. 2.
Monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) expression in normal human prostatic epithelial (E-PZ) and stromal (F-PZ) cells. (A) MAO-A transcript levels in E-PZ cells are much higher than those in F-PZ cells, as determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. (B) MAO-A protein is readily detectable in E-PZ cells by Western blotting analysis, whereas little or no MAO-A protein is measurable in F-PZ cells. (C–H) Expression pattern of proteins of interest in E-PZ cells by immunocytochemistry: (C) MAO-A shows a punctuate staining pattern in the cytoplasm, (D) K14, a basal cell marker, is expressed in the cytoplasm, (E) p63, a basal cell marker, is expressed in the nuclei, and (F) K18, a marker of transit amplifying cells and secretory cells, is expressed in the cytoplasm. E-PZ cells are negative for secretory cell markers including AR (G). The proliferative nature of E-PZ cells is shown by labeling with Ki67 (H). The magnification for (C–H) is × 200. For all images, the size bar is 100 µM.