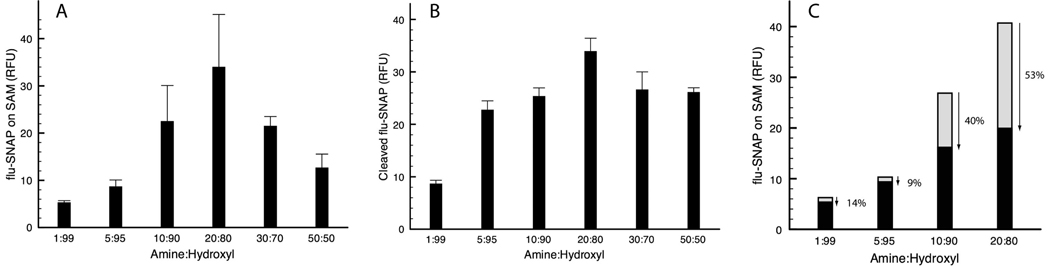
Figure 4.
(A) Surface density as qualitatively related to scanned fluorescence intensity at 520 nm (50 µm resolution). (B) Extent of ALC cleavage with respect to mixed monolayer composition. SAMs comprised of varying ratios of amine:hydroxyl headgroups were exposed to 20 µg/mL ALC. Fluorescence intensity of solution removed from microwells was quantified in a standard plate reader. (C) Flu-SNAP SAMs of (1–20% amines) were either exposed to ALC (20 µg/mL) or a HEPES control buffer without toxin in microchannels. The extent of cleavage was determined by comparing pixel intensities. The most fluorescent monolayer (20% NH2) corresponded to the highest rate of ALC enzyme activity at the surface.