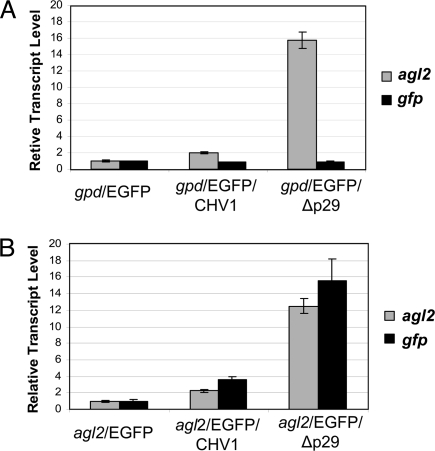
Fig. 4.
Response of an agl2-promoter/EGFP-reporter to virus infection. C. parasitica strains gpd/EGFP and agl2/EGFP produced by transformation of wild-type strain EP155 with promoter/reporter plasmids pCNE2GP and pA2PG, consisting of the C. parasitica glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd) promoter or the agl2 promoter, respectively, fused to the EGFP coding domain (see Materials and Methods), were infected with full-length hypovirus CHV1-EP713 or the mutant hypovirus Δp29 that lacked the p29 suppressor of RNA silencing. The accumulation levels of gfp transcripts and native agl2 transcripts were determined by real-time RT-PCR (Materials and Methods). (A) The level of gfp (black columns) and native agl2 (gray columns) transcript accumulation are shown for a representative gpd-promoter/EGFP-reporter strain following infection by CHV1-EP713 (gpd/EGFP/CHV1) or the Δp29 mutant virus (gpd/EGFP/Δp29) relative to the levels found in the virus-free gpd-promoter/EGFP-reporter control strain set to a value of one. (B) A similar analysis is shown for a representative agl2-promoter/EGFP-reporter strain.