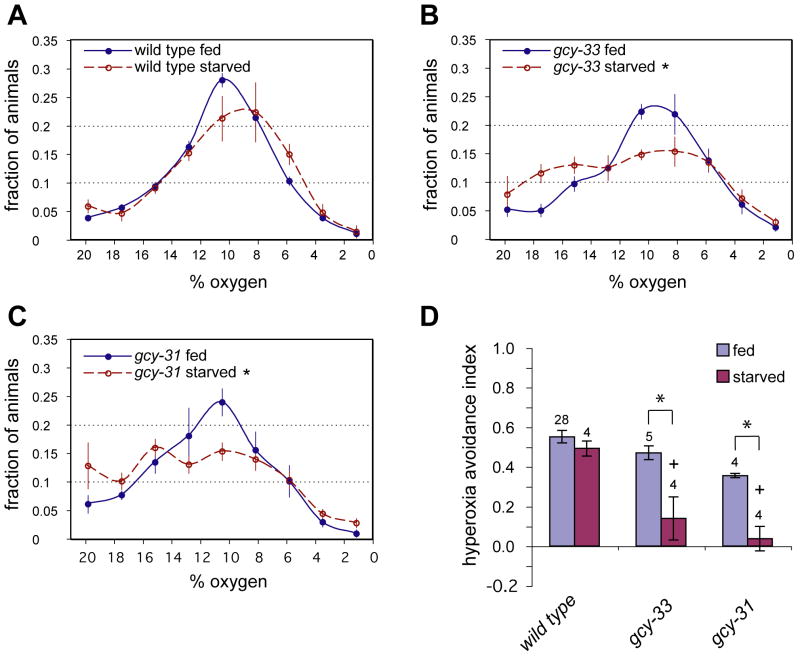
Figure 6. GCY-31 and GCY-33 promote aerotaxis in starved animals.
(A–C) Distributions of fed and starved animals in gradients of 0% to 21% O2. About 80–100 animals per assay were allowed to distribute through a device with a linear O2 gradient, and their positions were scored after 25 minutes. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM). (A) Wild type. (B) gcy-33(ok232) mutants. (C) gcy-31(ok296) mutants. (D) The hyperoxia avoidance index describes the preferential accumulation of animals in the middle three bins (7–14% O2) compared to the left three bins (14–21% O2), and is calculated as [(# at 7–14%)−(# at 14–21%)]/(# in 7–21%). Error bars indicate SEM. Asterisks indicate significance by t-test, P < 0.05. Crosses indicate significance by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post test using N2 starved as control group (P < 0.05). The numbers of experiments performed are indicated.