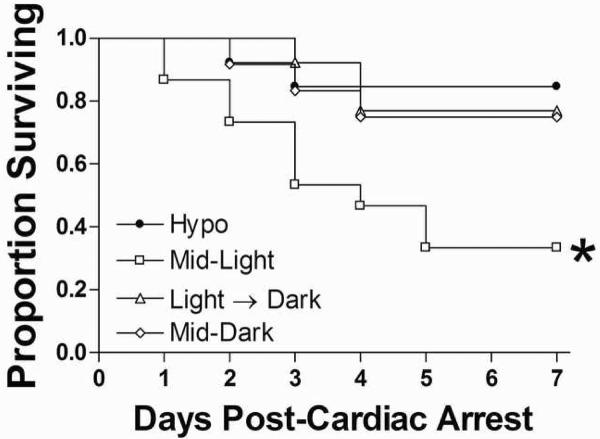
Figure 1. Time-of-day determines cardiac arrest survival.
Cardiac arrest reduced survival in normothermic mice that underwent CA/CPR during the Mid-Light period. Eighty-four percent of mice in the hypothermic groups survived CA/CPR. Among the normothermic groups, mice in the Light→Dark transition group and the Mid-Dark group survived at 76.9% and 75%, respectively. In contrast, only 33% of mice that underwent CA/CPR during the light period (Mid-Light group) survived to day 7 post-reperfusion. Thus, timing of CA/CPR significantly altered survival (Kaplan-Meier Survival Analysis; χ2=10.19, p<0.05). *Significantly different from all other groups at p<0.05.