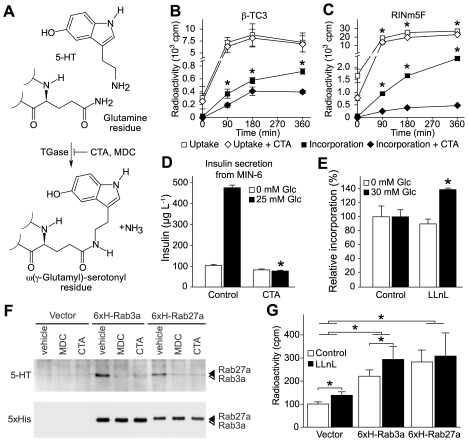
Figure 4. Inhibition of protein serotonylation reduces insulin secretion.
(A) Scheme of protein serotonylation of glutamine residues by TGase. Cysteamine (CTA) and monodansylcadaverin (MDC) are potent inhibitors of TGases. (B and C) Uptake and protein incorporation of [3H]-5-HT in β-TC3 (B) and RINm5F cells (C) in the presence of CTA (500 µM; 3 h). *p<0.05; n = 3. (D) Insulin secretion from MIN-6 cells in the presence of CTA (500 µM; 3 h). *p<0.05; n = 4. (E) Proteasomal degradation of serotonylated proteins in RINm5F cells at different glucose concentrations in the presence or absence of the proteasomal inhibitor LLnL (50 µM; 3 h).*p<0.05; n = 4. (F) Immunoblot of serotonylated (5-HT) and total (5xHis) 6xH-Rab3a (white arrowhead) and 6xH-Rab27a (black arrowhead) prepared from glucose-stimulated RINm5F cells treated with 100 µM MDC, 200 µM CTA, or vehicle. Shown is one representative experiment out of three repetitions. (G) Quantification by Ni-NTA pull-downs of 6xH-Rab3a and 6xH-Rab27a from glucose-stimulated RINm5F cells incubated with [3H]-5-HT and either 50 µM LLnL or vehicle. *p<0.05; n = 3. Vector, vector-transfected control. For (B–E) and (G), data are means ± SEM.