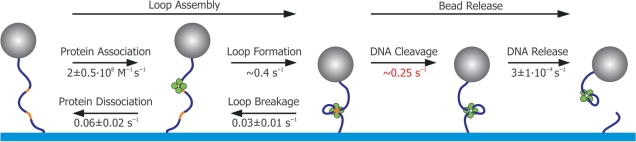
Figure 7.
Reaction pathway of SfiI revealed by combining TPM and solution kinetics. The reaction pathway for DNA cleavage by SfiI can be separated in two stages. The first stage, loop assembly, involves protein association and loop formation: both of these steps are reversible as the protein can let go of one site (to release the loop) or dissociate completely from the DNA. The second stage is irreversible: the DNA is cleaved by the protein and eventually SfiI releases the cleaved DNA. With TPM we obtain all the rates of the first stage in a single measurement (black numbers show corrected values, see ‘Discussion’ section). From the solution kinetics experiments, we find the DNA cleavage rate (red number). Finally, from the TPM cleavage experiments, we acquire the DNA release rate (black number, see ‘Discussion’ section) and complete the whole kinetic scheme. The values obtained by TPM for protein association and dissociation, and for the release of the cleaved DNA, all concur with values acquired from bulk solution kinetics.