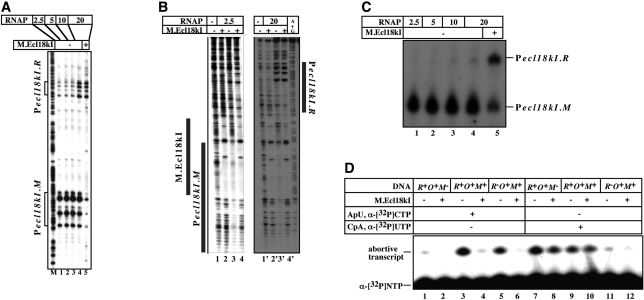
Figure 6.
In vitro transcription and promoter complex formation from ecl18kI promoters in the presence of increasing concentrations of RNAP. (A–C) Increasing amounts of E. coli RNAP σ70 holoenzyme were combined with a DNA fragment containing the entire ecl18kI intergenic region and the flanking sequences in the absence (lanes 1–4) or in the presence (lane 5) of M.Ecl18kI. In (A), promoter complexes were probed with KMnO4; in (B), promoter complexes were footprinted with DNase I; in (C), a single round of transcription was allowed to occur by supplementing the reactions with a mixture of NTPs and heparin. Reaction products were resolved by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and revealed by autoradiography. (D) RNAP was combined [at high ratio corresponding to lanes 4 and 5 in (A)] with indicated wild-type or mutant ecl18kI intergenic DNA fragments and abortive transcription initiation reactions characteristic of Pecl18kI.R or Pecl18kI.M were initiated in the presence of in the absence of M.Ecl18kI. Reaction products were resolved by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and revealed by autoradiography.