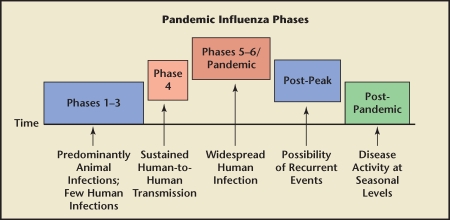
Figure 2.
The World Health Organization (WHO) phases of a worldwide pandemic are shown. Phase 1 is when viruses in animals do not cause infections in humans. Phase 2 is when animal viruses are known to cause infection in humans, but this is a rare event. Phase 3 is when animal viruses cause sporadic cases in humans, but where there is very limited or no subsequent human-to-human transmission. Phase 4 is when human-to-human transmission has been verified and is able to cause community-level outbreaks; this level indicates a significant increase in risk of a pandemic. Phase 5 refers to human-to-human transmission documented in at least 2 countries in 1 WHO region; this level represents a strong signal that a pandemic is imminent. Phase 6 refers documented human-to-human transmission and community-level outbreaks in at least 2 countries in different WHO regions; this level indicates a global pandemic. The post-peak phase refers to a decrease in disease levels, but uncertainty as to whether additional waves of disease will occur; previous pandemics have been characterized by several waves of activity over a period of months. The post-pandemic phase refers to return of disease levels to those seen under normal conditions.