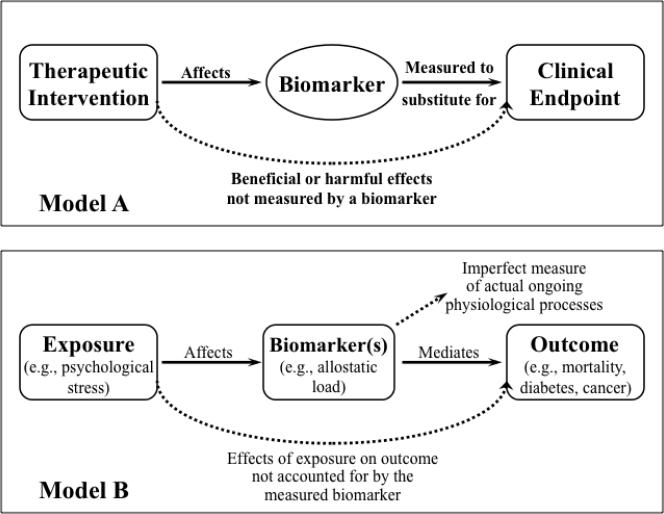
Figure 1.
Model A, upper panel, delineates the role of biomarkers as mediators for effects of therapeutic interventions on clinical outcomes (in this case, specifically for clinical trials). Redrawn from(Biomarkers Definitions Working 2001), p. 93. Model B, lower panel, emphasizes the place of biomarkers in mediating pathways from exposure to outcome, but also highlights complex exposures (e.g., stressors), integrative biomarkers (e.g., allostatic load), chronic (e.g., diabetes) or multifactorial (e.g., mortality) outcomes, and measurement uncertainty. Redrawn with minor modification from (Loucks et al. 2008), p. 526.