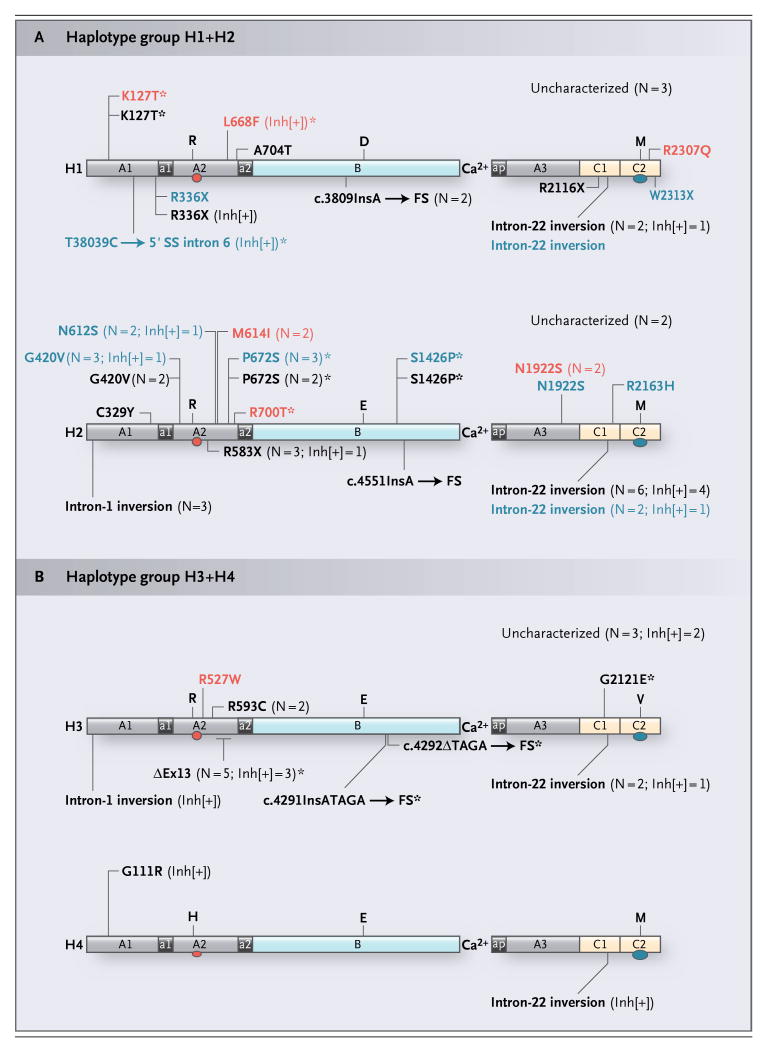
Figure 2. Hemophilic Mutations and the Four Wild-Type Factor VIII Proteins Predicted to Be Encoded by the Background F8 Haplotypes on Which They Were Identified.
For factor VIII, the two immunodominant-inhibitor epitopes located in the A2 domain (red oval) and the C2 domain (blue oval) are shown. Mutations found in patients with either an H1 or an H2 haplotype (H1+H2) are shown in Panel A, and mutations found in patients with either an H3 or an H4 haplotype (H3+H4) are shown in Panel B. For all haplotypes, missense mutations are shown above the appropriate factor VIII protein, and the other mutation types are shown below. Missense and nonsense mutations are indicated by their residue positions in the mature factor VIII protein. The point mutation T38039C, which occurs at position +2 of the 5′ splice site (SS) of intron 6, is designated according to the genomic nucleotide numbering system used for the F8 reference sequence.17 The positions of four frameshift (FS)-inducing small deletions and insertions are numbered according to their locations in the full-length F8 complementary DNA (c) with respect to the transcription start site.24 Specifically, one deletion (c.4292ΔTAGA) and three insertions (c.3809InsA, c.4551InsA, and c.4291InsATAGA) are indicated by the number of the wild-type nucleotide positioned immediately 5′ of the mutation site. ΔEx13 indicates an in-frame deletion of the 210-bp exon 13 sequence and an unknown amount of flanking nonexonic sequences from introns 12 and 13. For those mutations that occurred in more than one patient, whether or not the patients were related, the number of times any given abnormality was observed (N) is indicated in parentheses. All previously unknown mutations are indicated with an asterisk. The baseline severity of hemophilia for each patient is shown by the color of the text defining his mutation, with black, blue, and red indicating severe, moderate, and mild disease, respectively. For those mutations found in at least one inhibitor-positive (Inh[+]) patient, the number of patients with a given abnormality in whom inhibitors developed is also indicated in parentheses. A 3′-terminal partial gene deletion involving exons 24, 25, and 26 in two inhibitor-positive brothers is not shown. D, E, H, M, R, and V denote the amino acids aspartic acid, glutamic acid, histidine, methionine, arginine, and valine, respectively.