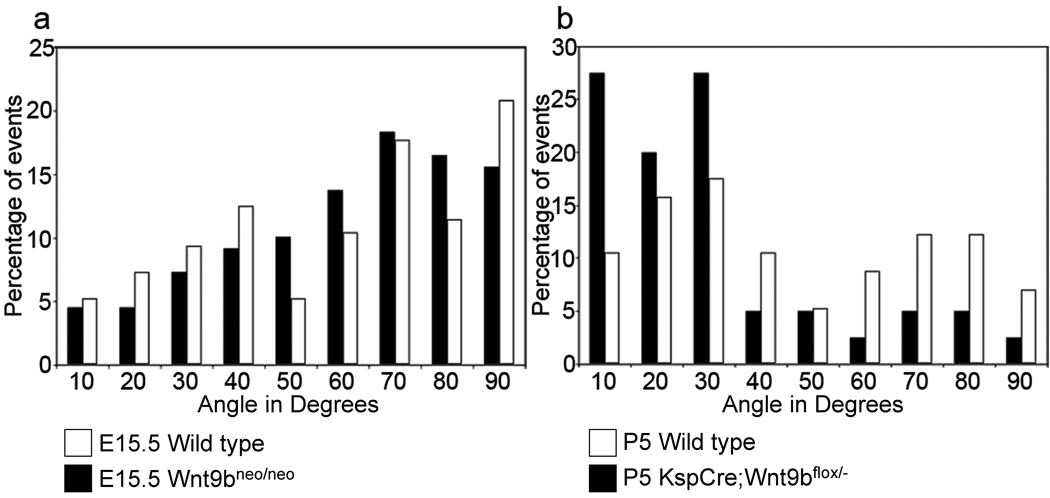
Figure 3. Cell division becomes oriented after birth in a Wnt9b–dependent process.
(a) Graphical representation of the angle between the mitotic spindles and the longitudinal axis of DBA-positive tubules at E15.5 indicates that cell division in both wild type (black bars) and Wnt9bneo/neo tubules (white bars) is randomly oriented at E15.5 when compared to the expected random distribution by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test. P > 0.55 for both wild type (N=109) and mutant (n=96). (b) At P5, the orientation of dividing cells in KspCre;Wnt9b−/flox DBA positive cells (white bars, n=50) is significantly different (p < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U test) from wild type (black bars, n=45) indicating that Wnt9b is necessary for orientation of cell division that occurs post-natally.