Fig. 1.
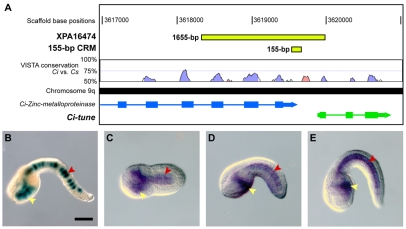
The cis-regulatory activity of the XPA16474 sequence recapitulates the expression of the gene that it flanks. (A) Mapping of the XPA16474 sequence (green rectangle at the top) to the Ciona intestinalis genome shows that this fragment covers the last three exons (rectangles) and intervening introns (thin lines) of the Ci-Zinc-metalloproteinase gene (ci0100137797), as well as an intergenic region and the first exon of a neighboring gene, which we named Ci-tune (ci0100137819). The location of the minimal 155-bp CRM (detailed in Fig. S2 in the supplementary material) is also shown (smaller green rectangle). VISTA phylogenetic footprint (http://pipeline.lbl.gov/cgi-bin/gateway2) of this region in Ciona intestinalis and Ciona savignyi was performed employing the following parameters: calculation window, 100 bp; minimum conservation width, 100 bp; conservation identity, 50%. Conserved coding regions are depicted as blue peaks, conserved non-coding sequences as pink peaks. (B) X-Gal staining of a late-tailbud Ciona embryo electroporated at the one-cell stage with the 1655-bp XPA16474 sequence. (C-E) Detection of Ci-tune transcripts by WMISH reveals expression in the notochord and trunk endoderm at (C) early-tailbud, (D) mid-tailbud and (E) late-tailbud stages. In B, D and E, embryos are oriented with anterior to the left and dorsal up; C is a ventral view, anterior to the left. Yellow arrowheads indicate endodermal cells; red arrowheads, notochord cells. Ci, Ciona intestinalis; Cs, Ciona savignyi. Scale bar: 50 μm.