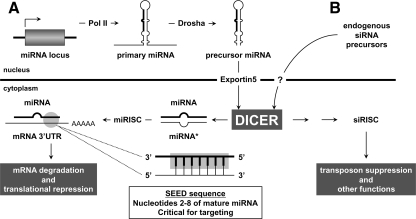
Figure 7.
Dicer-dependent synthesis of miRNAs and endogenous siRNAs. A, miRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II to generate primary transcripts. These transcripts are cropped by the DROSHA/DGCR8 Microprocessor complex to yield approximately 70-nt precursor miRNAs, which are exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by Exportin 5. There, the DICER complex processes the precursor into a 21- to 23-nt duplex consisting of the mature miRNA and its antisense. The mature miRNA is preferentially loaded into the miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC), which mediates pairing with complementary sequences in the 3′ UTR of target mRNA transcripts, leading to mRNA degradation and translational repression. The specificity of targeting is especially dependent on nucleotides 2–8 of the mature miRNA, known as the seed sequence. B, Endogenous siRNAs are synthesized from long, double-stranded RNA precursors derived from repetitive sequences, sense-antisense pairs, or inverted repeats that form hairpins. It is unknown whether endogenous siRNA precursors use Exportin 5 to translocate to the nucleus; however, once in the cytoplasm they are processed by the DICER complex into 21- to 23-nt duplexes. Mature siRNAs are incorporated into the siRNA-induced silencing complex (siRISC), which is similar to the miRISC but may also have unique components. Endogenous siRNAs function in transposon suppression and other functions such as pseudogene regulation of founding source mRNAs.