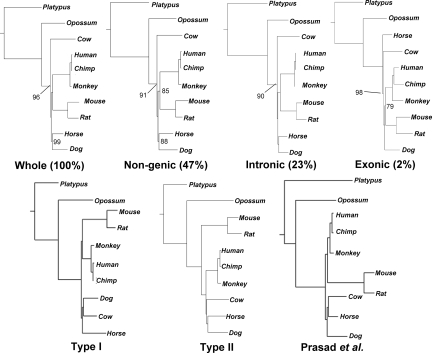
Fig. 2.
Similar evolutionary information in genic and nongenic genome partitions. (Upper) FFP mammalian species trees created from whole, nongenic, intronic, and exonic genome partitions have identical tree topologies with slight differences in internal branch lengths. For each neighbor-joining FFP tree, the optimal feature length is l = 18. Clade frequencies <100% (from 1,000 replicates) are indicated. (Bottom) For comparison, the two major types (I and II) of individual gene-tree topologies are shown. A tree from Prasad et al. (11) based on a large-genome-scale gene alignment is also shown for comparison. Note that only species common among the three methods are used for comparison (some taxa were pruned from their tree for consistent comparison. (% values indicates the average fraction of the whole genome. Note that 28% are genic regions which are neither intron nor exon).