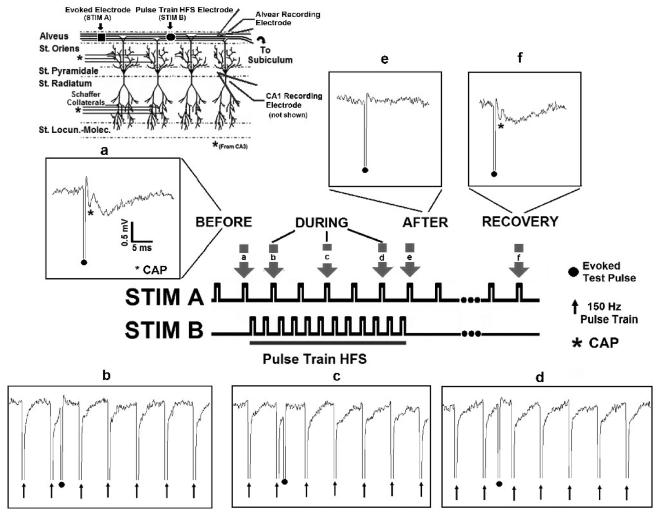
Fig. 9. Pulse train HFS blocks axonal conduction in-vitro.
Evoked test pulses were generated by a stimulating electrode placed in the alvear axon field. An independent electrode, located in the alveus, applied the pulse train HFS. Field potentials were recorded extracellularly in the alveus and CA1 somatic layer (see inset describing hippocampal network). (a) A robust evoked response (CAP, denoted by asterisk) was generated by STIM A (0.5 Hz) before HFS. Pulse train HFS (STIM B, 500 μA, 150Hz) blocks axonal conduction. Insets, b through d (evoked response, STIM A,). (e, f) Evoked responses (CAP) generated by STIM A are depressed following termination of HFS, but recover over ~ 60 seconds following HFS termination (n=8).