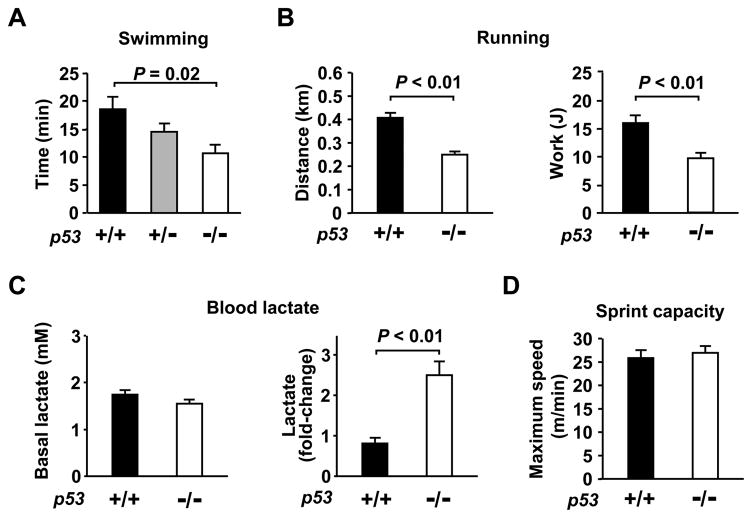
Figure 1.
Aerobic exercise capacity is p53 dependent. A, Effect of p53 gene dose on maximum swimming duration (min). p53 genotype: +/+ (black); +/− (gray); −/− (white). One-way ANOVA, P < 0.05. B, Maximum treadmill running capacity in p53+/+ (dark) and p53−/− (light) mice expressed as distance (km) and work (J) (n = 6–8 each). C, Measurements of resting blood lactate levels (mM) under resting conditions (left panel) and after sub-maximum exercise (fold-change of resting state) (right panel), n = 9 each, mean ± SEM. D, Similar sprint capacity as measured by maximum treadmill speed tolerated by p53+/+ (dark) and p53−/− (light) mice, n = 9 each.