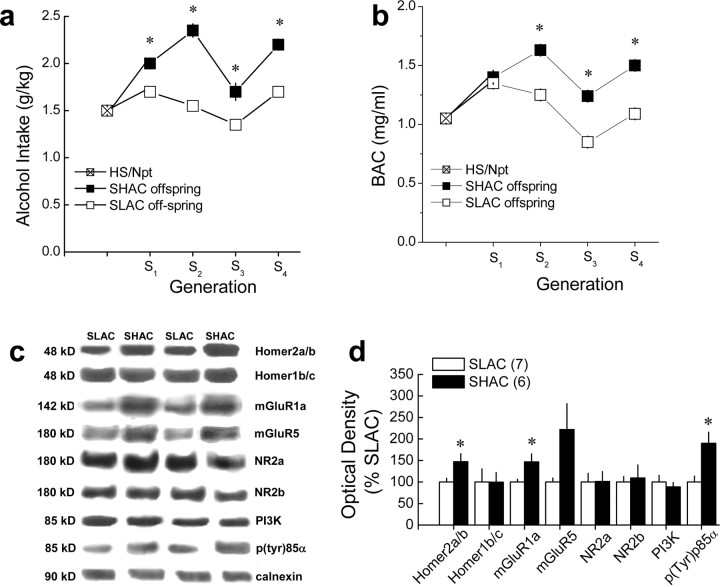
Figure 8.
Line differences in NAC Homer2 and PI3K activity in selectively bred SHAC and SLAC mice. a, b, Summary of the average alcohol dose consumed (grams per kilogram; a) and BACs (b) attained after the second session of 30 min alcohol drinking (selection phenotype) in the genetically heterogeneous HS/Npt mice (foundation population for the selection) and in the SHAC and SHAC offspring, across four generations of selective breeding. Data in a and b represent the mean ± SEM of 80–104 mice per line per generation; *p < 0.05, SHAC offspring versus SLAC offspring. c, Representative immunoblots for the total protein levels of Homer2a/b, Homer1b/c, mGluR1, mGluR5, NR2a, NR2b, PI3K, p(Tyr)p85α PI3K binding motif [p(Try)p85α], and calnexin (loading control) in the NAC of fourth generation (S4) selectively bred SHAC and SLAC mice, at 3 months after their second 30 min alcohol-drinking session. d, Summary of the line differences in protein expression, expressed as a percentage of average levels of SLAC animals. Data in d represent the mean ± SEM of the number of mice indicated in the figure. *p < 0.05 versus SLAC (t tests).