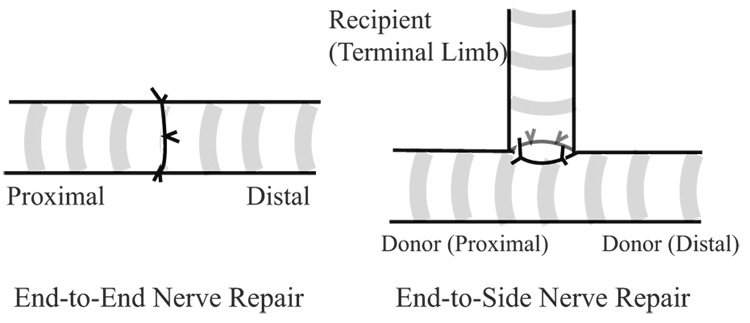
Figure 1.
In end-to-end repair, the transected nerve is reapproximated and secured with microsurgical technique. If the proximal stump is unavailable for end-to-end repair, one option is to coapt the recipient (terminal) limb of the distal transected nerve to the donor nerve in an end-to-side (ETS) fashion. The basal lamina tubes of the terminal limb remain structurally contiguous with motor endplates and sensory receptors.