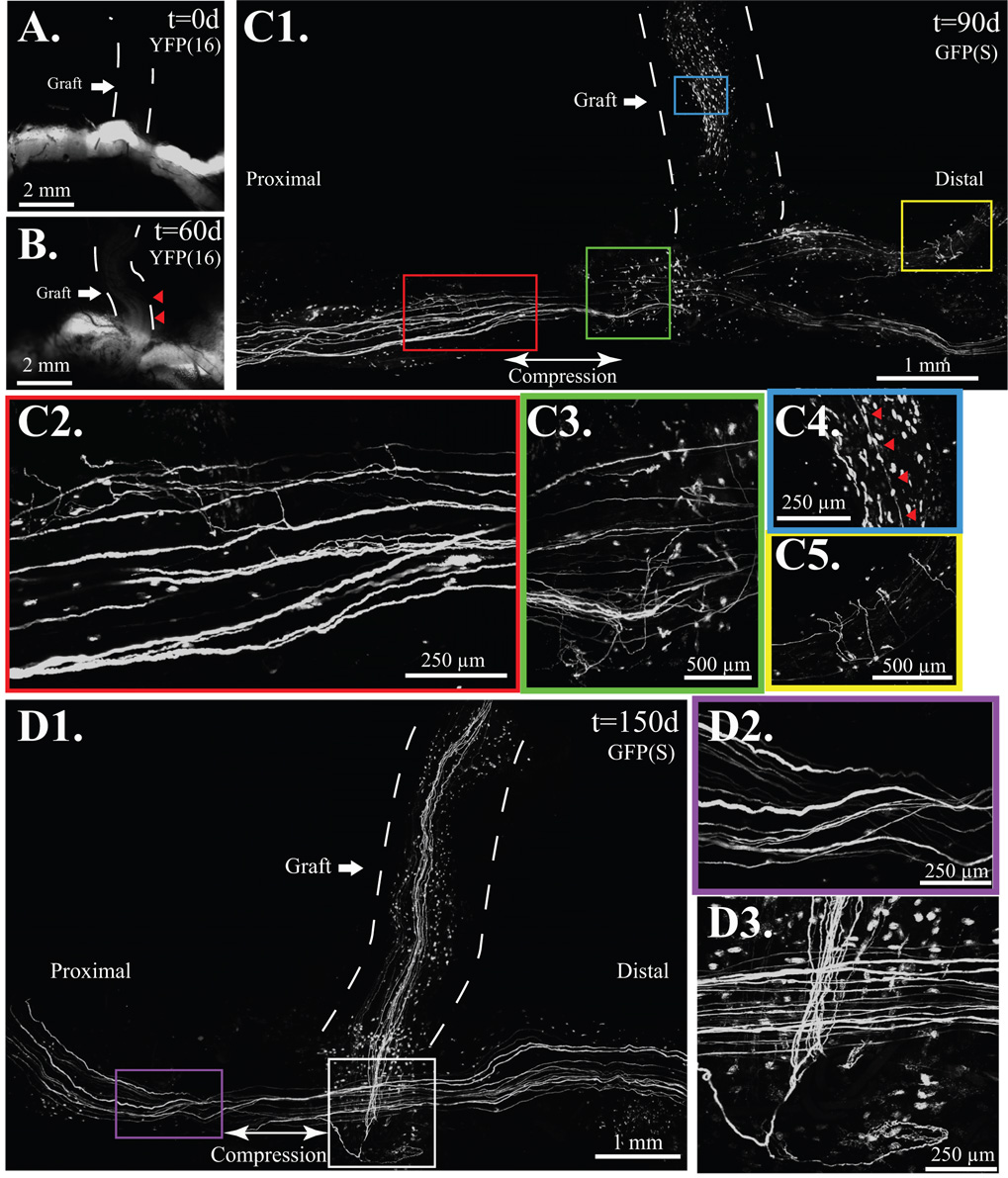
Figure 4. Compressive ETS repair resembles the atraumatic technique but with proximal compression.
A. The fluorescent-naïve median nerve graft, marked is by a dashed line. B. At 60 days, axons are noted in the proximal graft marked by red arrows in mThy-YFP(16) mice. C1. By 90 days, regenerative sprouts, shown here under confocal microscopy on a fixed mThy1-GFP(S) specimen, were noted along the length of the donor nerve and recipient limbs. C2. Axonal sprouts proximal, C3. and distal to compression. C4. A few axons, marked by red arrows noted in the previously fluorescent naïve graft. C5. Multiple regenerative sprouts noted distal to the ETS repair. D1. Numerous graft-based axons noted by 150 days, D2. but proximal (shown here) and distal sprouting, noted at 90 days, absent by 150 days. D3. Sprouts were confined to the region of ETS repair at 150 days.