Figure 1.
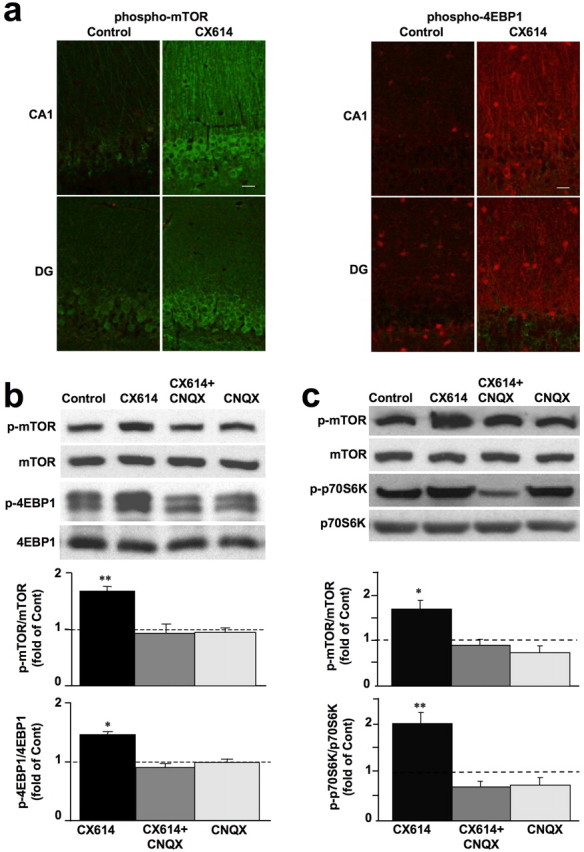
Effects of CX614 on mTOR and 4EBP1 phosphorylation in acute hippocampal slices and primary cortical neurons. a, Acute hippocampal slices from adult male rats incubated with vehicle (Control) or CX614 (50 μm) for 1 h were immediately processed for immunohistochemistry with antibodies against phospho-mTOR (left panels) or phospho-4EBP1 (right panels). Note the clear increase in immunoreactivity in stratum radiatum of CA1 and in stratum granulosum of the dentate gyrus (DG) in CX614-treated slices compared with control. Scale bar, 20 μm. b, Acute hippocampal slices from adult male rats were incubated with CX614 (50 μm) for 1 h in the presence or absence of CNQX (50 μm), and tissues were immediately processed for immunoblots with the following antibodies: phospho-mTOR, mTOR, phospho-4EBP1, and 4EBP1. c, Cultured cortical neurons were incubated with CX614 (10 μm) for 1 h in the presence of CNQX (25 μm) and were processed for immunoblotting with the following antibodies: phospho-mTOR, mTOR, phospho-p70S6K, and p70S6K. Immunoblots were quantified and ratios of phosphorylated over total antigens were calculated; data were then expressed as fold of control and are means ± SEM from six independent experiments. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001 compared with control (ANOVA followed by Tukey's posttest analysis).
