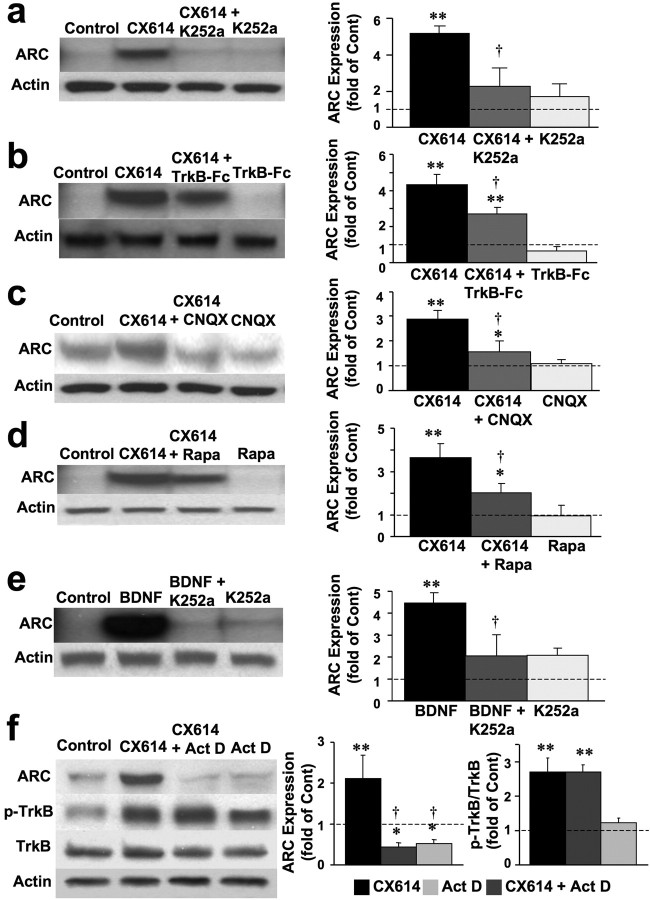
Figure 7.
BDNF mediates CX614-induced stimulation of ARC synthesis in primary neuronal cultures. Cultured cortical neurons were incubated in the absence or presence of CX614 (10 μm) and K252a (0.5 μm, a), TrkB-Fc (0.5 μg/ml, b), CNQX (50 μm, c), or rapamycin (Rapa) (100 μm, d) for 1 h. At the end of treatment, cells were processed for immunoblotting with antibodies against ARC and actin (for loading control). Immunoblots were quantified and corrected ARC levels were calculated; data were then expressed as fold of control and are means ± SEM from six independent experiments. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001 compared with control; †p < 0.01 compared with CX614 (ANOVA followed by Tukey's posttest analysis). Cultured cortical neurons were incubated in the absence or presence of BDNF (50 ng/ml) and K252a (0.5 μm) (e). At the end of treatment, cells were processed for immunoblotting with antibodies against ARC and actin (for loading control). Immunoblots were quantified and corrected ARC levels were calculated; data were then expressed as fold of control and are means ± SEM from six independent experiments. **p < 0.001 compared with control; †p < 0.01 compared with CX614 (ANOVA followed by Tukey's posttest analysis). f, Cultured cortical neurons incubated in the absence or presence of CX614 (10 μm) and actinomycin D (Act D) (10 μm) for 1 h. At the end of treatment, cells were processed for immunoblotting with antibodies against ARC, total and phosphorylated TrkB, and actin (for loading control; data not shown). Immunoblots were quantified and corrected ARC levels and ratios of phosphorylated over total TrkB were calculated; quantification of the blots from six independent experiments indicated that the effects of CX614 were highly significant, and the effects of CX614 on ARC but not on phospho-TrkB were significantly reduced by actinomycin D. Cont, Control.